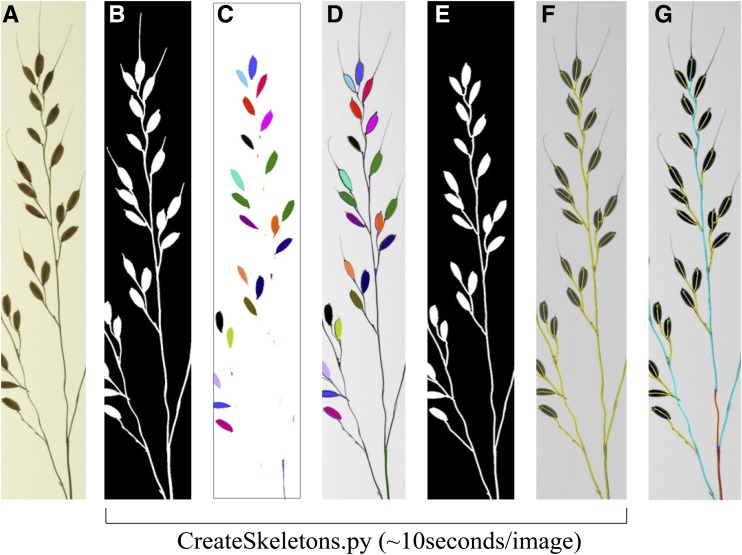
Figure 3.
Schematic depicting awn removal using exact morphological erosions. A, Raw image of a panicle branch. B, Initial binary image after segmentation. C, Erosion of the image at 0.032 cm using the Euclidean distance transform. The binary components of the image object that remain after erosion are labeled with distinct colors. D, Binary components are superimposed over the original panicle image and reconnected by the darkest path (i.e. branches and rachis axis). E, After path reconnection, the awnless binary image is used to calculate the final skeleton. F, Panicle skeleton (yellow) superimposed over axes. All segmentation and skeletonization steps (B–F) are controlled by the CreateSkeletons.py script. G, Final panicle skeleton after the use of DefineMainAxis.py and ExtractInfo.py.