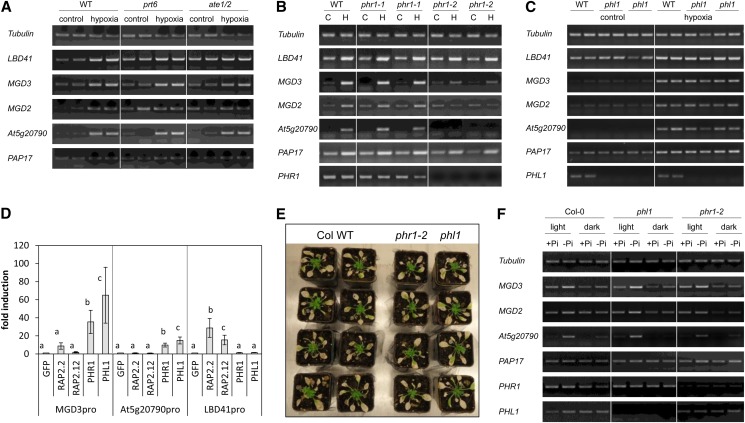
Figure 4.
The shoot-specific hypoxia response is dependent on PHR1. A, Expression of selected hypoxia-responsive genes after treatment of seedlings with hypoxia for 4 h in light. One prt6 and one ate1/ate2 mutant line (Gibbs et al., 2011) were compared to the wild type (WT). One representative experiment of three independent experiments is shown with two individual samples. B, Expression of selected hypoxia-responsive genes after treatment of seedlings with hypoxia (H) for 4 h in light or without hypoxia treatment (control [C]). Two different phr1 mutant lines were compared to the wild type, and seeds from two individual homozygous plants were used for each mutant line. One representative experiment out of three independent experiments is shown. C, Expression of selected hypoxia-responsive genes after treatment of seedlings with hypoxia for 4 h in light. One phl1 mutant line with seeds from two different homozygous plants was compared to the wild type. One representative experiment out of two independent experiments is shown with two individual samples. D, Promoter activity assay for two shoot-specific hypoxia-responsive promoters (MGD3pro and At5g20790pro) and one core hypoxic promoter (LBD41pro). Protoplasts were transformed with a promoter::Luciferase construct and either GFP or a transcription factor. Luciferase activity was normalized to the reference vector p70SRUC, and the fold change was calculated in comparison to GFP. Different letters represent significant differences at P < 0.05 from eight biological replicates (Tukey’s honestly significant difference mean-separation test). E, Survival of the wild type and phr1-2 or phl1 mutants under submergence. Four-week-old plants were submerged for 4 weeks in a short-day rhythm. Photos were taken after 2 weeks of recovery. The experiment was performed together with the one shown in Figure 2. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. F, Expression of selected hypoxia-responsive genes after growth of wild-type (WT), phl1, and phr1-2 seedlings on phosphate-deficient medium in light or darkness. The experiment was performed seven (wild type) or two (mutants) times, and one representative experiment is shown. In A, B, D, and F, the photos show the RT-PCR bands separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and after staining with Serva DNA stain G.