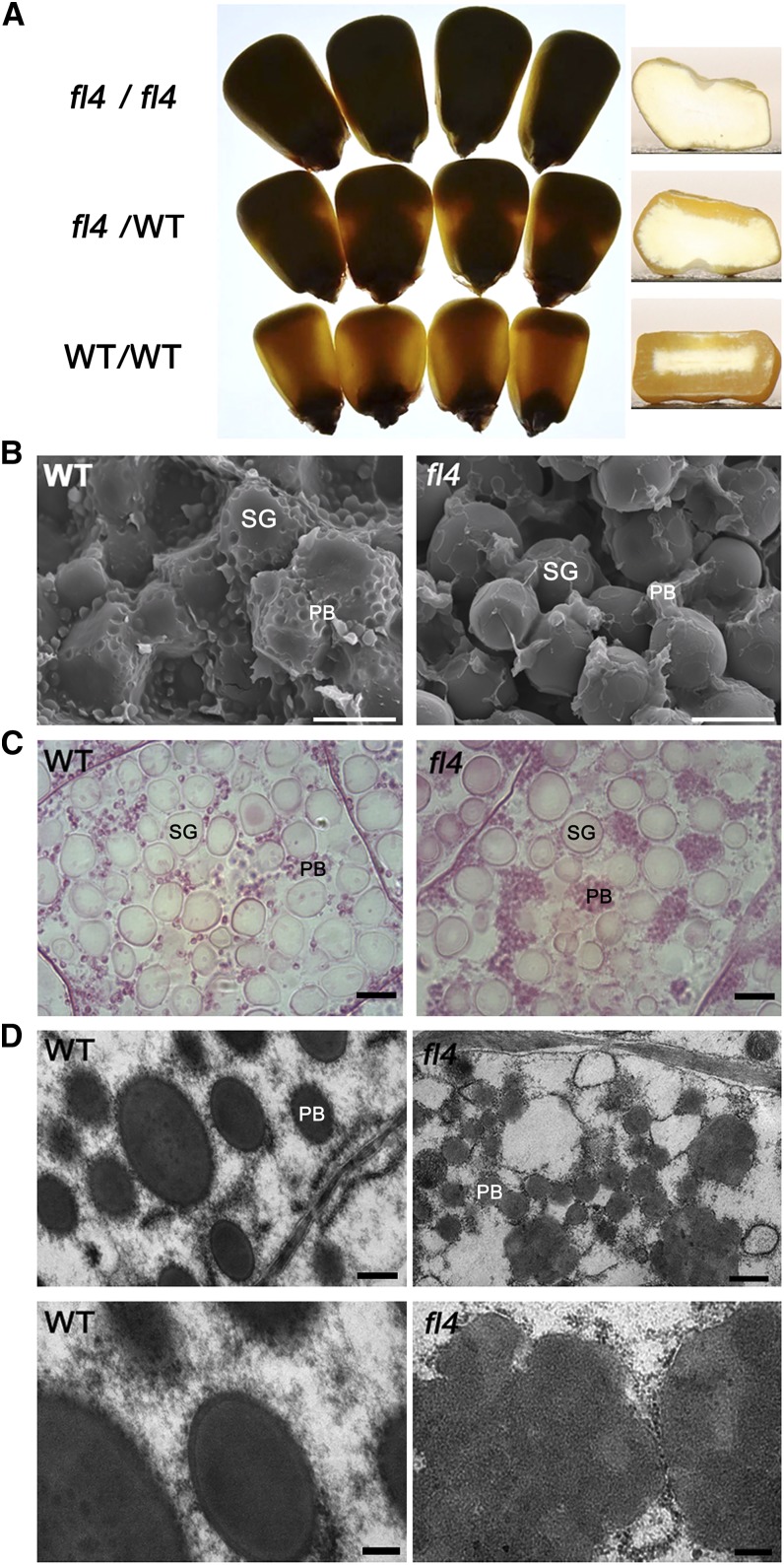
Figure 1.
Phenotypic features of maize fl4 mutants. A, Light transmission by mature kernels. The homozygous mutant kernels (fl4/fl4), heterozygous kernels (fl4/wild type [WT]), and homozygous wild-type kernels (wild type/wild type) were randomly selected from segregating F2 population and viewed on a light box. B, Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the peripheral regions of mature wild-type and fl4 endosperm. PB, Protein body; SG, starch granules. Bars = 10 μm. C, Microstructure of developing endosperms of the wild type and fl4 (20 DAP). Protein bodies were adjoined into clumps in fl4 (right). PB, Protein body; SG, starch granules. Bars = 5 μm. D, Ultrastructure of developing endosperms of the wild type and fl4 (20 DAP). Small, misshapen, and aggregated protein bodies were observed in fl4 (right). Top, Low magnification. Bottom, High magnification. PB, Protein body; SG, starch granules. Bars = 500 nm (top) and 200 nm (bottom).