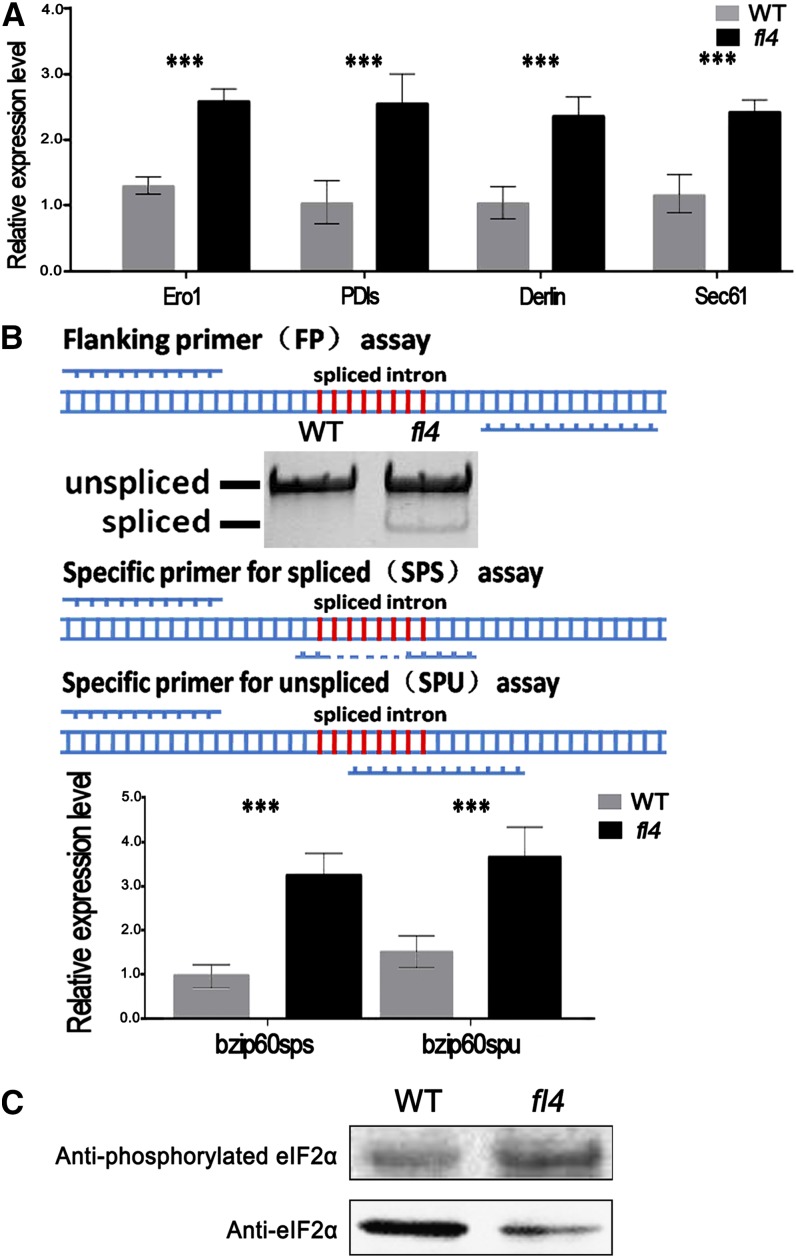
Figure 6.
Effects on ERAD, UPR, and the phosphorylation of eIF2α in fl4. A, Expressions of ERAD-associated genes ERO1 (GRMZM2G108115), PDIs (GRMZM2G389173), ZmDerlin1-1 (GRMZM2G117388), and Sec61 (GRMZM2G130987) were examined in the wild type (WT) and fl4 by real-time PCR analysis (19 DAP). Values are the mean values with se (n = six individuals; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t test). B, RNA samples from wild-type and fl4 kernels (19 DAP) were analyzed for the presence of unspliced and spliced ZmbZIP60 mRNA by reverse transcription-PCR using the flanking primers (FP) assay. The level of ZmbZIP60 expression and splicing were analyzed by real-time PCR using primers for unspliced bZIP60 mRNA (SPU) or for spliced mRNA (SPS). Values are the mean values with se (n = six individuals; ***P < 0.001, Student’s t test). C, Immunoblot comparing the phosphorylated eIF2α accumulation in wild-type and fl4 kernels (18 DAP). Anti-eIF2α was used as control.