Fig. 4.
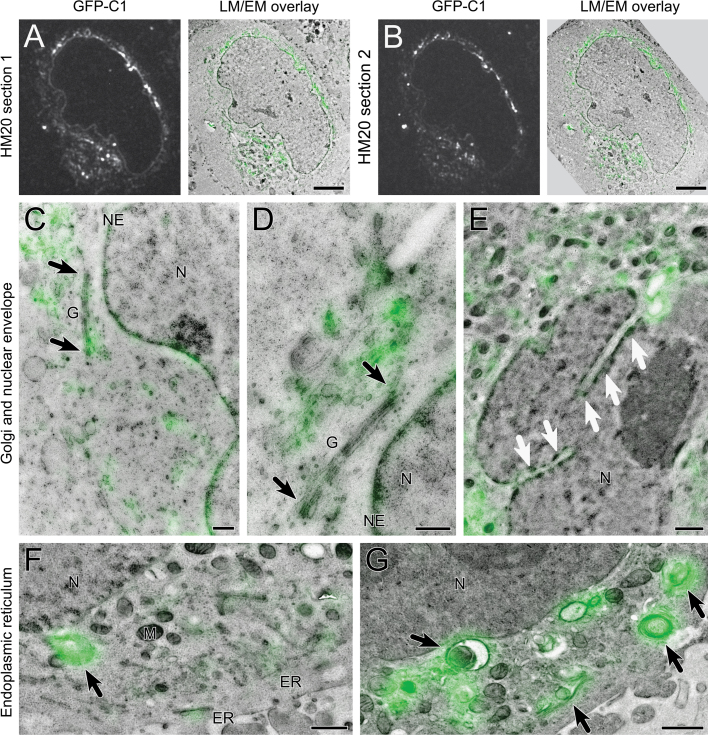
CLEM of GFP-C1 and mCherry-H2B in HeLa cells using post-embedding light microscopy. GFP-C1 fluorescent signals overlaid onto electron micrographs of the corresponding region using the IRF method. (A) Image of GFP-C1 signal alone imaged under dry conditions, and overlaid directly onto the matching electron micrograph, for a cell embedded in HM20. The fluorescent signal corresponds to the nuclear envelope, and other structures within the cytoplasm (higher magnification micrographs of subcellular detail are shown in Fig. 5). (B) An adjacent section through the cell shown in A. (C–E) Increased precision of GFP-C1 localisation to Golgi stacks (G) and the NE. In (C), black arrows indicate localisation of fluorescent signal to the highly curved tips of Golgi cisternae. An enlarged view from an adjacent section is shown in (D). Localisation to the NE is also evident. In (E), white arrows indicate localisation of fluorescent signal to the nucleoplasmic reticulum. (F, G) Localisation of GFP-C1 to endoplasmic reticulum and to membrane stacks (black arrows) in cells expressing low (F) and high (G) levels of the GFP-C1 construct. ER: endoplasmic reticulum, G: Golgi, M: mitochondrion, N: nucleus, NE: nuclear envelope. Scale bars—A, B: 5 μm, C, D: 500 nm, E-G: 1 μm.