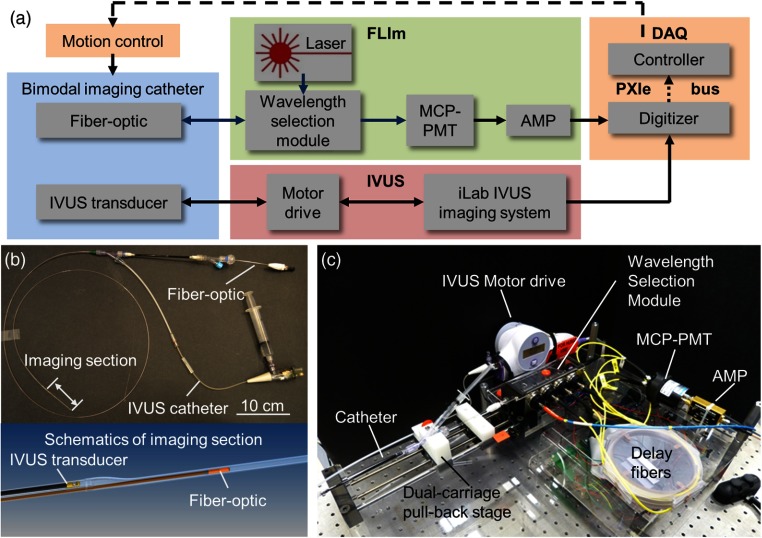
Fig. 1.
Bimodal system schematic. (a) Fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIm) subsystem: UV pulses from the laser are sent through a dichroic within the wavelength selection module (WSM) into the catheter’s fiberoptic. The fluorescence emission is collected by the same fiberoptic, directed back into the WSM that spectrally resolves the emission, detected by a multichannel plate photomultiplier (MCP-PMT), and amplified by a preamplifier (AMP). IVUS subsystem: Boston Scientific iLab IVUS imaging system consists of an integrated motor drive that rotates a single element 40-MHz IVUS transducer (retrieved from Atlantis SR Pro coronary imaging catheter) at a constant speed of 1800 rpm. Bimodal imaging catheter: IVUS transducer and side-viewing fiberoptic integrated in a parallel design. [see (b)] Data acquisition (DAQ) and control module: Digitizer records analog signals from both FLIm and IVUS subsystems and upload the data to the embedded controller through PXIe bus. The controller communicates with motion controllers in charge of the catheter’s helical scanning motion. (b) Completed assembly of the bimodal catheter and the imaging section. Fiberoptic and IVUS transducer enter the imaging section sequentially to perform helical scanning. (c) Photo of the compact assembly of catheter, motion control, and FLIm/IVUS system components.