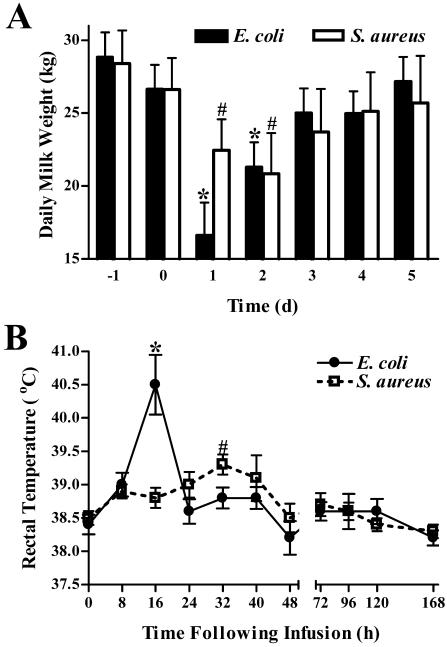
FIG. 2.
Effects of intramammary infection with E. coli or S. aureus on daily milk weights and temperatures. (A) Total milk weight (sum of morning and evening outputs) data were collected 1 day prior to infection (−1), the day of infection (0), and for 5 days following infection. The vertical bars represent the means (plus standard error) of milk weights. * and #, significantly decreased compared to prechallenge levels (day −1) in cows challenged with E. coli or S. aureus, respectively (P < 0.05). (B) Rectal temperatures were measured immediately prior to and at various times following intramammary infection as an indicator of the systemic response. Mean (± standard error) temperatures are shown. * and #, significantly increased compared to time zero in cows challenged with E. coli or S. aureus, respectively (P < 0.05).