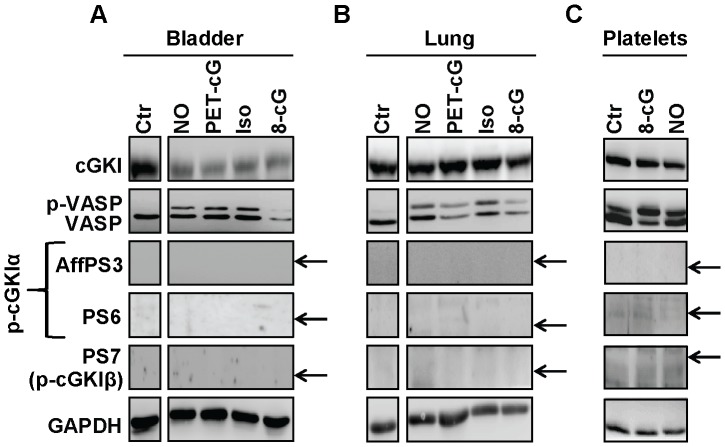
Figure 5. Analysis of N-terminal cGKI phosphorylation in native mouse tissues and platelets.
(A) Bladder and (B) lung were rapidly isolated from wild-type mice and then incubated in Tyrode buffer for 15 min at room temperature under control conditions (Ctr) or in the presence of 100 nM calyculin A and 0.1 mM DEA-NONOate (NO), 1 mM 8-Br-PET-cGMP (PET-cG), 0.01 mM isoprenaline hydrochloride (Iso), or 1 mM 8-Br-cGMP (8-cG). (C) Platelets were isolated from wild-type mice and incubated for 10 min at 37°C under control conditions (Ctr) or in the presence of 1 mM 8-Br-cGMP (8-cG) or 3 mM DEA-NONOate (NO). Lysates (22 µg for bladder, 30 µg for lung, and equal fractions by volume for platelets) were subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. GAPDH was used as loading control. The arrows indicate the positions expected for phospho-cGKI species as determined by co-loading of purified proteins on the same gel. The displayed results are representative for three independent experiments.