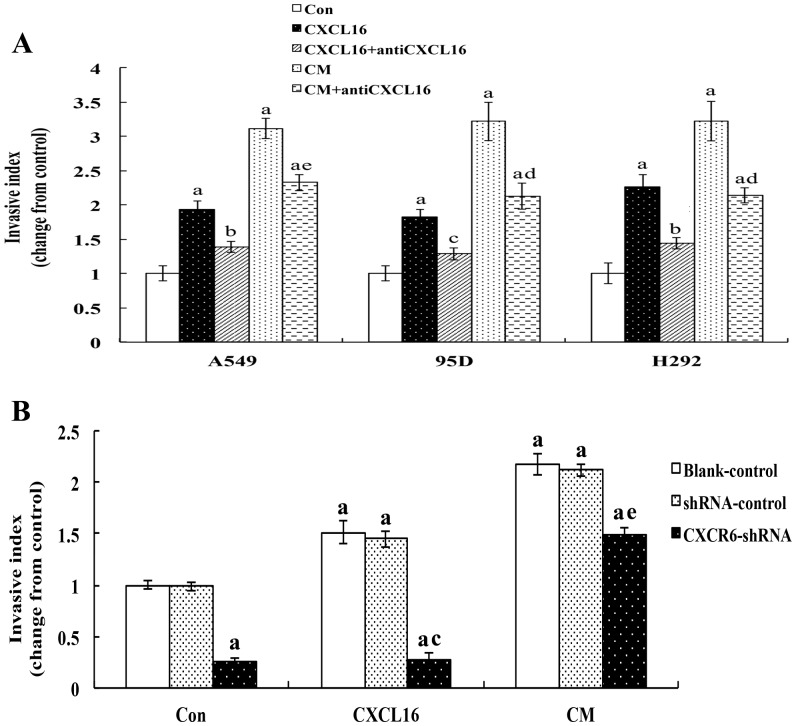
Figure 9. CXCL16 induces migration and invasion of lung cancer cell lines in vitro.
Invasion assay was employed to investigate the effects of CXCL16-CXCR6 axis on the invasive ability of A549, 95D and H292 cells in vitro. Firstly, the isolated A549, H292 or 95D cells (1×105/200 µl serum-free 1640) were plated in the upper chamber, and treated with CM, CXCL16 (100 ng/ml) or a combination of CM or CXCL16 with CXCL16 neutralization antibody(100 ng/mL). Secondly, the A549 cells, from the blank-control, phU6/GFP/Neo-CXCR6 and phU6/GFP/Neo group, were seeded on the upper chamber at a density of (1×105/200 µl serum-free 1640), then treated with CXCL16 (100 ng/ml) or CM. The cells migrated to the lower surface were counted and the invasive index was calculated as the proportion of the migrated cells of the experiment group to that of its own control. Error bars depict the standard error of the mean. Con: the control; CXCL16: treated with 100 ng/ml CXCL16; antiCXCL16: treated with 100 ng/mL CXCL16 neutralizing antibody; CM: conditioned medium for A549, 95D or H292; Blank-control: without any treatment, shRNA-control: phU6/GFP/Neo; CXCR6-shRNA: phU6/GFP/Neo-CXCR6 (2819-1). aP<0.01 compared to the vehicle control; bP<0.05, cP<0.01, compared to the CXCL6 alone; dP<0.05, eP<0.01compared to the CM treatment group.