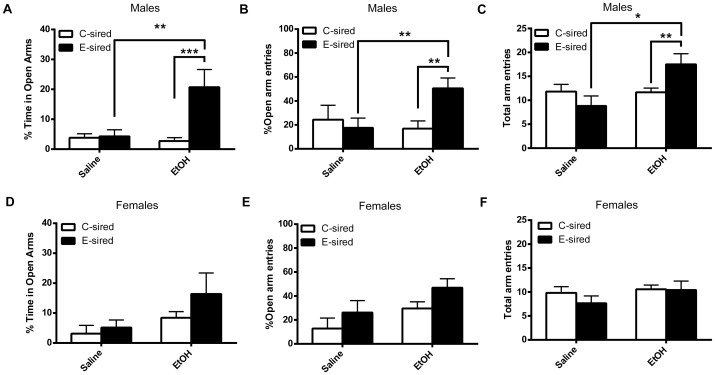
Figure 4. Offspring were tested for EtOH-induced anxiolysis by comparing performance on an elevated plus maze 10 minutes after i.p. injection of 1 g/kg EtOH or saline.
(A) E-sired male offspring spend greater time in open arms after treatment with EtOH compared to C-sired male offspring and E-sired male offspring treated with saline; E-sired male offspring treated with EtOH also have (B) increased percent of open arm entries and (C) total arm entries relative to C-sired male offspring and E-sired male offspring treated with saline. There were no significant differences between E- and C-sired females treated with EtOH or saline on (D) time spent in open arms, (E) percent open arm entries, or (F) total arm entries. n = 6–7/group, data presented as mean ± SEM, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.