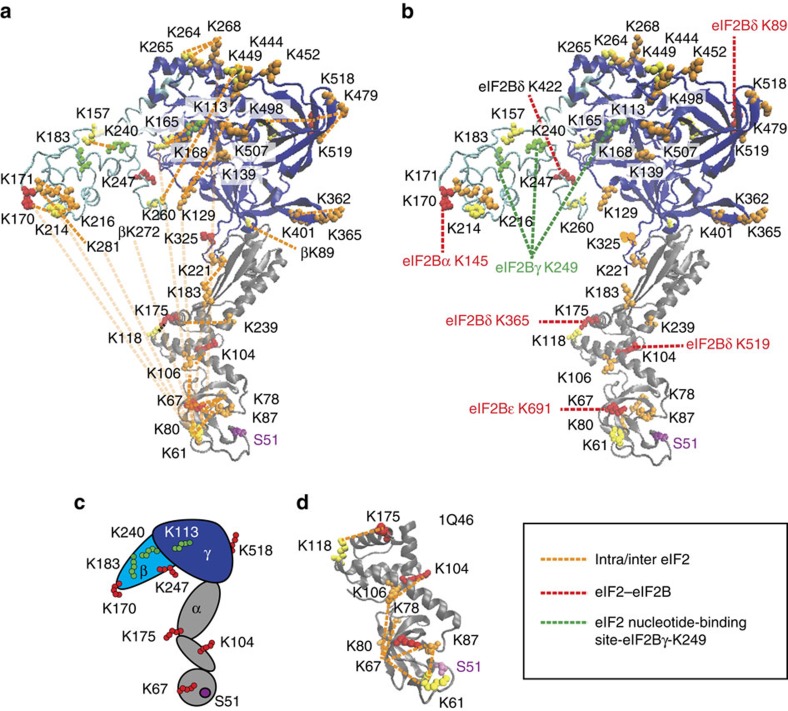
Figure 3. Homology model of yeast eIF2 with identified cross-links.
(a) Homology models for eIF2 α- (grey), β- (cyan) and γ- (blue) subunits were obtained from Swiss Model modelling server and are based on the crystal structure of archaeal aIF2 from S. solfataricus (PDB 3CW2) used as a template. The highly dynamic and flexible nature of eIF2 is apparent from the multiple cross-links observed. Cross-linked lysine residues are shown as coloured spheres, and identified intra- and inter-protein cross-links within eIF2 are shown as orange dashed lines; eIF2α Ser51, involved in regulation, is shown in magenta. (b) Homology models as shown in a. Inter-protein cross-links between eIF2 and eIF2B (red), and inter-protein cross-links between eIF2Bγ K249 and residues around nucleotide-binding site of eIF2 (green). (c) Cartoon representation of eIF2 with mapped inter-cross-linked residues. (d) Crystal structure of the N-terminal part of the eIF2 α-subunit from S. cerevisiae (PDB 1Q46) with identified cross-links and containing Ser51 (labelled as in Fig. 3a). Cross-links shown were obtained from different cross-linking experiments (Supplementary Tables 4 and 5).