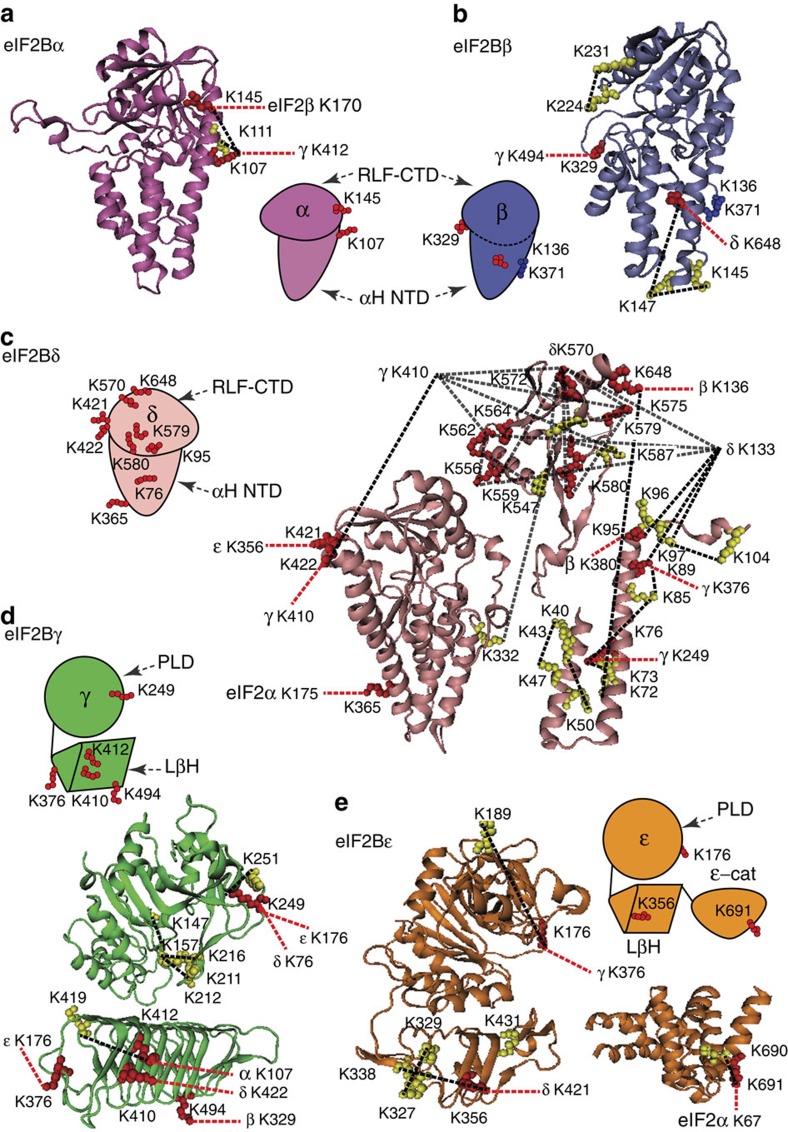
Figure 4. Homology model of yeast eIF2B subunits with identified cross-links.
(a) Homology model of the eIF2Bα (res. 1–304) based on the crystal structure of human eIF2Bα (PDB 3ECSA) and cartoon representation of the α-subunit with mapped intra- (yellow) and inter- (red) cross-linked residues. Cross-links are represented by dashed lines: intra, black; inter, red. (b) Homology model of the eIF2Bβ (res. 60–371) based on the crystal structure of human eIF2Bα (PDB 3ECSA) and cartoon representation of the β-subunit with mapped cross-linked residues (labelled as in Fig. 4a). (c) Homology models of the eIF2Bδ: residues 1–244 based on PDB 1YA9A template; residues 245–536 based on PDB 2YVKA template; residues 540–651 based on PDB 3A11A template and cartoon representation of the δ-subunit with mapped cross-linked residues (labelled as in Fig. 4a). (d) Homology models of the eIF2Bγ PL domain (res. 44–314) and LβH (res. 358–578) domains based on PDB 1YP2D and 2OI7A templates, respectively, and cartoon representation the γ-subunit with mapped cross-linked residues (labelled as in Fig. 4a). (e) Homology model of the eIF2Bε (res.30–431) based on PDB 1YP2A; the crystal structure of the catalytic domain ε-cat (res. 524–712) from S. cerevisiae (PDB 1PAQ) and cartoon representation of the ε-subunit with mapped cross-linked residues (labelled as in Fig. 4a). Cross-links shown were obtained from different cross-linking experiments (Supplementary Table 2).