Figure 4.
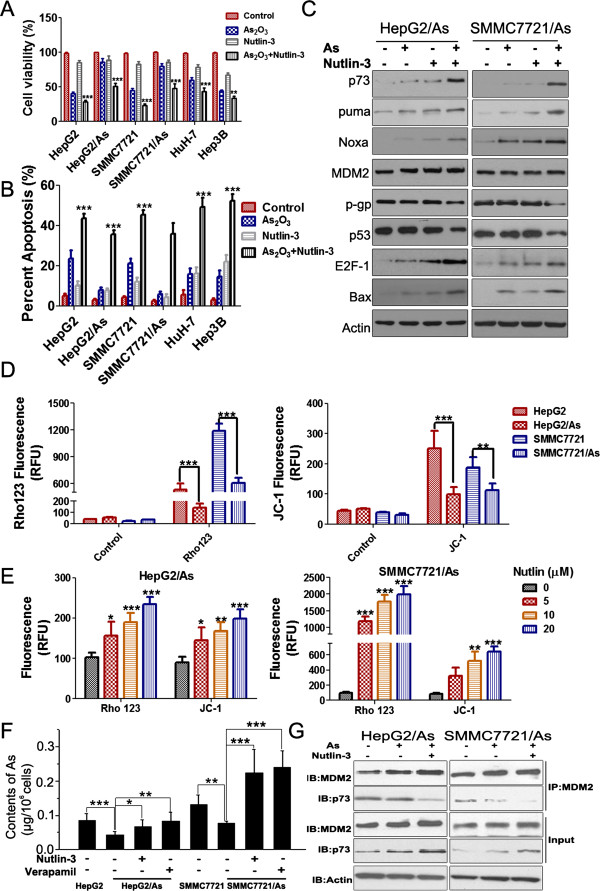
The synergetic effects of arsenic trioxide and Nutlin-3 on HCC resistant cells. (A and B) The concentration of arsenic trioxide applied here was 2 μM, and Nutlin-3 was 20 μM. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined after treatment for 48 h. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, versus cells treated with arsenic trioxide or Nutlin-3 alone. (C) Protein expression was compared among untreated, arsenic trioxide, Nutlin-3 and Nutlin-3/arsenic trioxide groups in HepG2/As and SMMC7721/As cells. Cells had been cultured in the medium without any arsenic trioxide for at least one week. The concentration of rhodamine 123 and JC-1 was 0.1 μM. (D) The fluorescence of rhodamine 123 and JC-1 in HepG2/As and SMMC7721/As cells. Cells were incubated with rhodamine 123 and JC-1 for 60 min, and for another 60 min to efflux. **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001. (E) The inhibition of efflux was depended on the concentration of Nutlin-3. Nutlin-3 at different concentration was added with rhodamin 123 or JC-1 into medium and incubated for 60 min. Rho123, rhodamine 123. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, versus control cells. (F) Nutlin-3 and R(+) verapamil assisted to increase the intracellular arsenic. All the cells were cultured with 2 μM arsenic trioxide, while treated groups were added 20 μM Nutlin-3 or 40 μM verapamil respectively and incubated for 2 h. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (G) Nutlin-3 inhibits binding of p73 to MDM2 when in combination with arsenic trioxide. Untreated cells, cells treated with 2μM arsenic trioxide, cells treated with 20 μM Nutlin-3, and cells treated with arsenic trioxide/Nutlin-3 combination for 24 h were immune-precipitated with an anti-MDM2 antibody. Immunocomplexes were subjected to immunoblotting with anti-MDM2 and anti-p73 antibodies.
