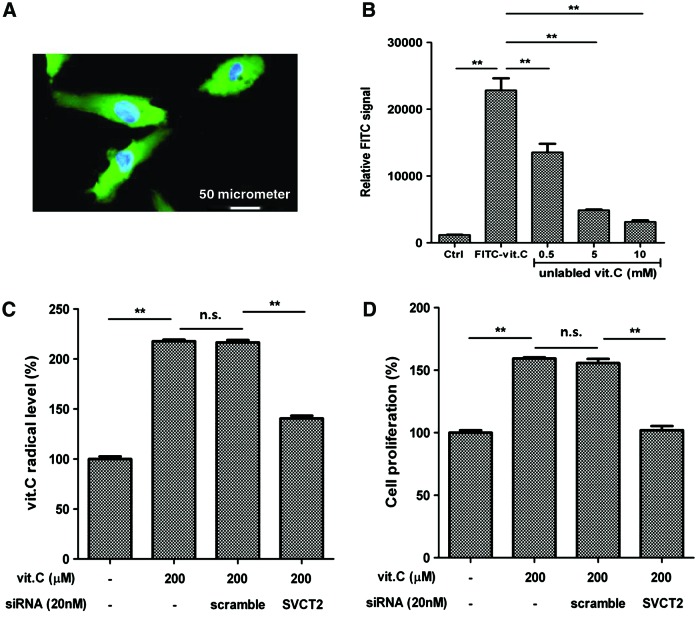
FIG. 2.
Sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 (SVCT2) mediates vitamin C uptake. Vitamin C uptake is mediated by SVCT2, which increases the proliferation of ASCs. (A) Fluorescence microscopy showed that FITC-labeled vitamin C was effectively incorporated into ASCs. The vitamin C signal (green) was high in the cytosol, but not in the nucleus (blue). (B) Fluorescence intensity decreased in the presence of unlabeled vitamin C, which suggests the existence of a vitamin C transporter. (C) The intracellular vitamin C concentration was measured using a vitamin C radical assay kit, and a siRNA specific for SVCT2 (20 nM) was transfected into ASCs. SVCT2 knockdown significantly reduced the intracellular vitamin C concentration in ASCs. (D) In addition, transfection of SVCT2 siRNA attenuated the vitamin C-induced proliferation of ASCs. Data are mean±STD (n.s., not significant; **P<0.01, Student's t-test). Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/scd