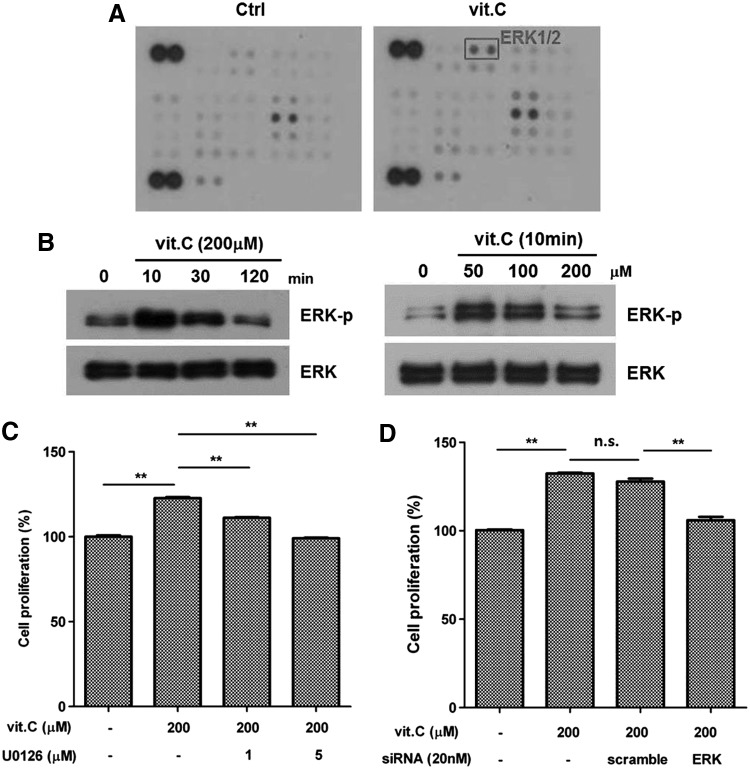
FIG. 3.
Vitamin C induces the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Vitamin C increased the phosphorylation of ERK1/2, and inhibition of the MAPK pathway attenuates the proliferation of ASCs. (A) In a phospho-kinase array, the ERK1/2 signal was highly induced by vitamin C treatment (200 μM for 10 min). (B) Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 increased in a time- and dose-dependent manner. (C) Treatment with a MAPK pathway inhibitor (U0216, 1–5 μM) reduced the vitamin C-induced proliferation of ASCs. (D) In addition, inhibition of ERK1 using siRNA (20 nM) reduced the vitamin C-induced proliferation of ASCs. Data are mean±STD (n.s., not significant; **P<0.01, Student's t-test).