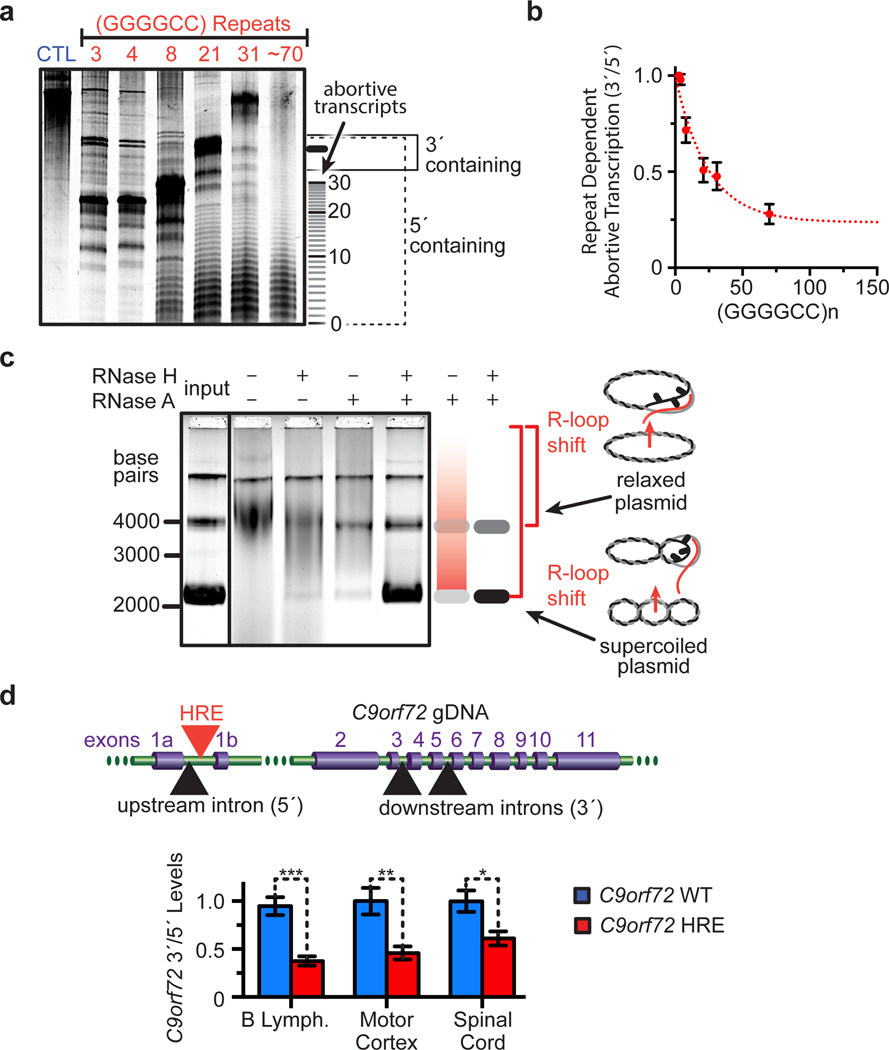
Figure 2. Abortive transcription in the C9orf72 HRE.
a) Increasing lengths of GGGGCC repeats cause accumulation of abortive transcripts in a length-dependent manner in vitro. The transcriptional products were separated on a denaturing gel with a 500 nt ssRNA control (CTL). b) Transcripts levels shown in (a) were densitometrically quantified and then plotted as the ratio of full-length transcripts that contain regions 3´ of the repeat divided by all transcripts that contain 5´ regions. The curve was fit to a single exponential. Data are means ± s.d. n = 4. c) The C9orf72 HRE induces the formation of R-loops on C9orf72 HRE-containing plasmids with (GGGGCC)~70. Treatment of the in vitro transcription products with RNase A and H digests the RNA still hybridized with relaxed or supercoiled plasmid and reduces the smearing that was caused by the size heterogeneity of RNA•DNA hybrids. Genomic DNA (top band) serves as an internal loading control. d) Patients carrying the C9orf72 HRE have reduced pre-mRNA 3´/5´ratios relative to C9orf72 WT, consistent with the HRE-induced abortive transcription reducing full-length transcript levels. Data are means ± s.e.m. n = 5/6 (B lymphocytes), n = 12/10 (motor cortex), n = 8/5 (spinal cord) for C9orf72 WT/HRE samples, respectively. ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05.