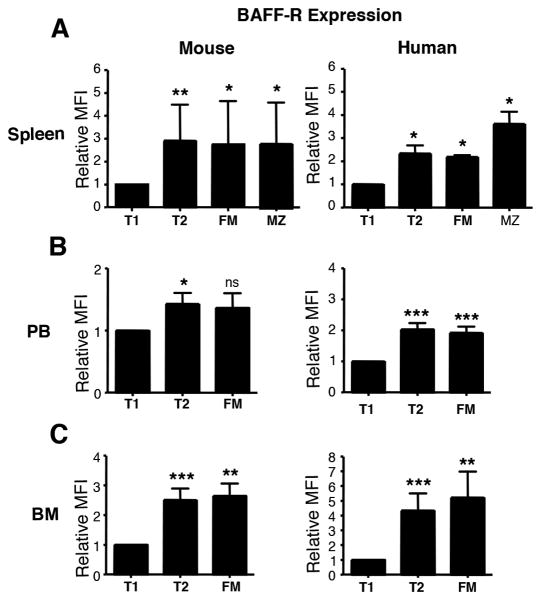
Figure 4. Patterns of differential BAFF-R expression are similar in mouse and human CD21/CD24 B cell subsets.
A-C, Mononuclear cells isolated from adult mouse and human spleen, PB, and BM were stained for IgM, CD21, CD24, BAFF-R and in human samples for CD27, CD38 and CD19 as well. IgM+ B cells falling in lymphocyte light scatter in mouse tissues were gated into CD21/CD24 subsets. Human PB, BM, and splenic T1, T2, and FM cells were gated as described in Fig. 3. For MZ cells in human spleen, CD19+IgM+ cells were assessed for CD21/CD24 MZ phenotype and this included both CD27+ and CD27− cells. For each tissue, graphed are the means + SEM of relative BAFF-R expression in each CD21/CD24 subset (normalized to BAFF-R levels in the T1 subset in that tissue). Data are from n=9 mouse spleen, n=7 mouse PB; n=9 mouse BM, n=4 human spleen, n= 15 human PB and n=9 human BM. Statistical differences are shown as *p < .05; **p< .01; *** and p < .001.