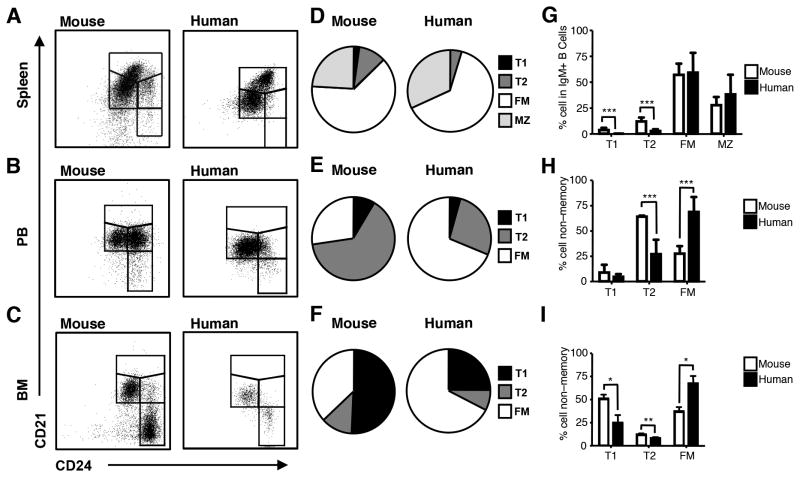
Figure 6. Transitional B cells are reduced in the non-memory B cell pool in humans as compared to mice.
Mononuclear cells were isolated from adult mouse and human spleen, PB, and BM. Cells were stained for IgM, CD21, CD24, and in human samples for CD27, CD38 and CD19 as well. A-C, IgM+ B cells falling in lymphocyte light scatter were gated in mouse tissues. For human spleen, CD19+IgM+ cells falling in lymphocyte light scatter were gated. Human PB and BM were gated as described in Fig. 3. CD21/CD24 gates are as shown. D, of the IgM+ B cell pool with respect CD21/CD24 subsets gated as described in results to include CD27+ and CD27− MZ cells. E-F. Pie graphs showing the composition of the non-memory B cell pool with respect CD21/CD24 subsets. G-I, Graphed are the mean ± SD of the percentages that each CD21/CD24 subset contributes to the IgM+ B cell pool in spleen and the non-memory B cell pool in PB and BM. Graphed are data from n=16 adult mouse spleen; n=6 adult mouse PB; n=9 adult mouse BM; n=4 adult human spleen; n= 33 adult human PB; and n= 11 adult human BM; Mice were adult male BALB/c and non-pregnant female C3H/HeN mice. Statistical differences between analogous subsets are shown as *p < .05; **p< .01; *** p < .001; and **** p< .0001.