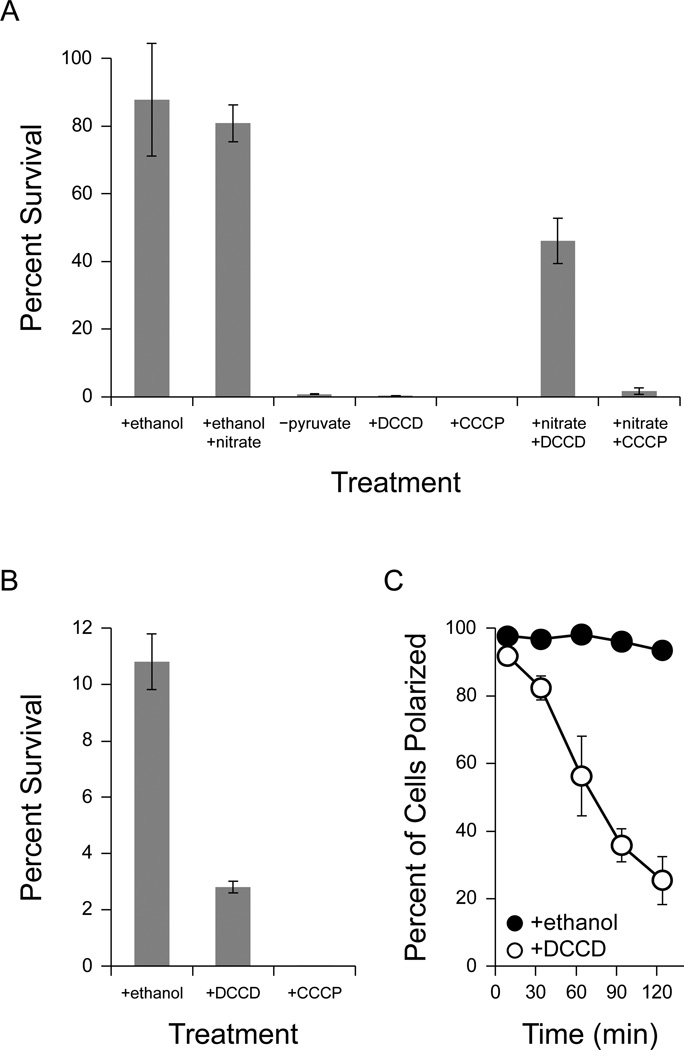
Figure 6.
Response of P. aeruginosa PA14 to drugs that disrupt the proton-motive force. Error bars represent the standard error of at least three independent experiments. 100% survival represents approximately 4 × 108 CFU/mL. (A) Anaerobic survival of P. aeruginosa PA14 after two days of anaerobic incubation with 40 mM pyruvate. At the start of anaerobiosis, potassium nitrate (50 mM), DCCD (2 mM), and/or CCCP (100 µM) were added as indicated. DCCD and CCCP were dissolved in ethanol, and so as a control ethanol was added to a final concentration of 0.2% where indicated. A culture incubated without pyruvate is shown for comparison (−pyruvate). (B) Anaerobic survival after two days of anaerobic incubation with 40 mM arginine. At the start of anaerobiosis, ethanol (0.2%), DCCD (2 mM), or CCCP (100 µM) were added as indicated. (C) Effect of DCCD on membrane polarization. After 24 hours of anaerobiosis, 2 mM DCCD was added to cultures surviving anaerobically on 40 mM pyruvate (+DCCD, open circles). Since DCCD was dissolved in ethanol, an equivalent concentration of ethanol (0.2%) was added to control cultures (+ethanol, closed circles). Membrane polarization was monitored over time as described in Methods (for an example analysis, see Supplemental Figure 5). Time 0 indicates the addition of DCCD and ethanol to the cultures.