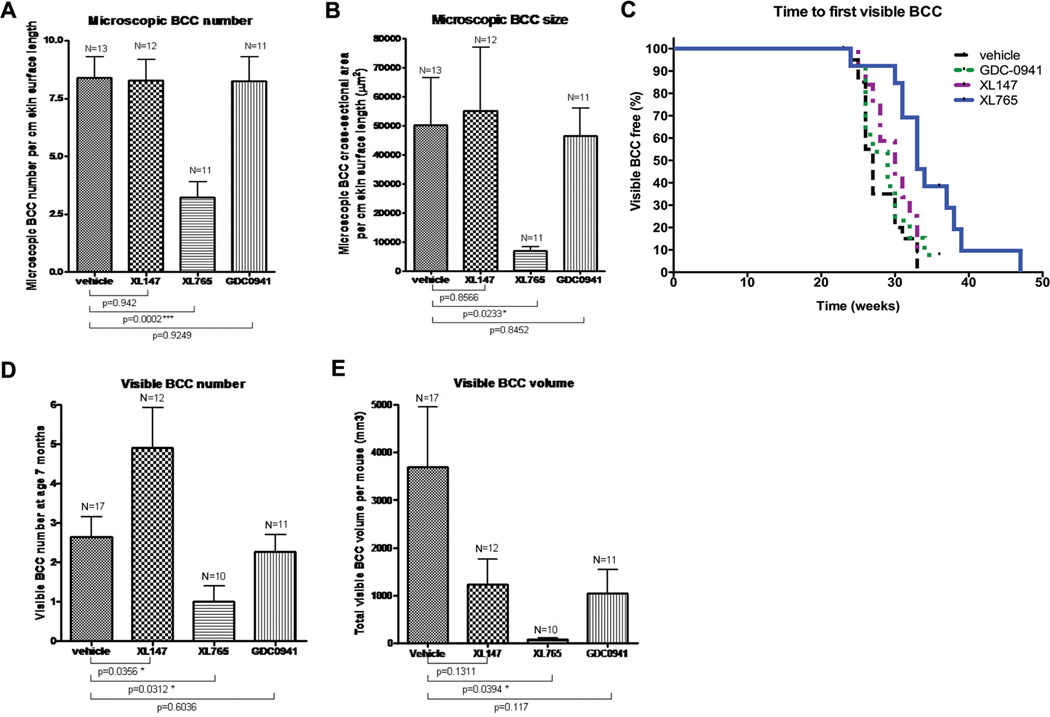
Figure 5. In vivo testing of therapeutically viable small molecule inhibitors of PI3K/AKT pathway for treating BCC.
(A, B) In vivo testing of therapeutically viable PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitors against microscopic and visible BCC assessment at age 21 and 28 weeks respectively, after 8 weeks of PI3K inhibitor treatment. For microscopic BCC assessment, dorsal skin biopsies of mice given oral formulations of PI3K inhibitors XL147, XL765 or GDC-0941 were analyzed to determine the microscopic BCC number (A) and size (B). Only XL765 demonstrated significantly chemopreventive efficacy against BCC number (*** p < 0.001, Student t test) and size (* p < 0.05, Student t test) compared to the vehicle control group. Mean and SEMs are shown.
(C) A Kaplan Meier graph showed the time to the appearance of the first visible BCCs. Only XL765-treated mice had a delay in the first visible BCC appearance, although it was not statistically significant. XL147 and GDC-0941 did not appear to have any effect on the rate of BCC tumorigenesis.
(D, E) Mice were assessed from age 28 weeks to determine the visible BCC number and size, respectively. Again, although different control vehicles were used, there were not significantly different from each other in terms of BCC numbers and size (data not shown), therefore the vehicle groups were combined. Only XL765 treatment reduced visible BCC number and volume by statistically significant amounts at the doses tested (* p < 0.05, Student t test). Mean and SEMs are shown.