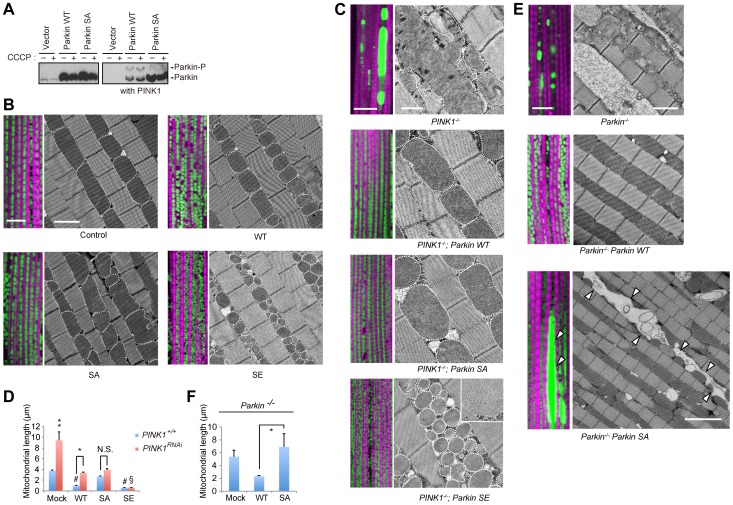
Figure 1. Phosphorylation of the Parkin Ubl domain regulates mitochondrial morphology.
(A) Parkin is phosphorylated by PINK1 in insect cells. S2 cells transfected with the indicated plasmids with or without Drosophila PINK1 were treated with or without 30 µM carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone (CCCP) for 1 h. The cell lysate was subsequently separated on a Phos-tag gel, followed by western blotting with anti-Drosophila Parkin. (B) The phosphorylation status of Parkin affects the mitochondrial length in muscle tissue. Fluorescent and TEM images of the indirect flight muscle in the indicated genotypes of 14-day-old adult flies are shown. To visualize the mitochondria, the mitoGFP (green) transgene was co-expressed, and the muscle tissue was counterstained with phalloidin (magenta). Mitochondria in the TEM images are outlined with broken lines to highlight their morphology. Scale bars = 10 µm in the fluorescent images and 2 µm in the TEM images. (C) Mitochondrial morphology of 14-day-old PINK1 mutant flies expressing mock, WT Parkin and phospho-mutants. The inset shows a high-magnification TEM image of PINK1-/-; Parkin SE with intact mitochondrial matrices. Scale bars = 10 µm in the fluorescent images and 2 µm in the TEM images. (D) The length of the long axis of the muscle mitochondria was calculated. The data represent the mean ± SE from three flies (n = 25 in each). ** p<0.01 vs. all other genotypes, # p<0.01 vs. mock with PINK1+/+, § p<0.01 vs. PINK1RNAi; WT or SA Parkin, * p<0.05, N.S., not significant. (E) Mitochondrial morphology of 14-day-old Parkin mutant flies expressing mock, WT or SA Parkin. Scale bars = 10 µm in all fluorescent images and 2 µm for Parkin-/- and WT Parkin; Parkin-/- and 5 µm for SA Parkin; Parkin-/- in the TEM images. Arrowheads indicate large mitochondrial aggregates. (F) The length of the long axis of the muscle mitochondria was calculated. The data represent the mean ± SE from three flies (n = 25 in each). * p<0.05. The genotypes are as follows: (B) UAS-mitoGFP/+; MHC-GAL4/+ (control), UAS-mitoGFP/UAS-Parkin; MHC-GAL4 (WT, SA and SE Parkin). (C) PINK1B9/Y; UAS-LacZ; MHC-GAL4 (PINK1-/-), PINK1B9/Y; UAS-Parkin; MHC-GAL4 (PINK1-/-; WT, SA or SE Parkin). UAS-mitoGFP; MHC-GAL4, UAS-PINK1 RNAi crosses were used rather than PINK1B9 crosses for fluorescent images. (E) UAS-mitoGFP/UAS-LacZ; Da-GAL4, ParkinΔ21/Parkin1 (Parkin-/-), UAS-mitoGFP/UAS-Parkin; Da-GAL4, ParkinΔ21/Parkin1 (Parkin-/-; WT or SA Parkin).