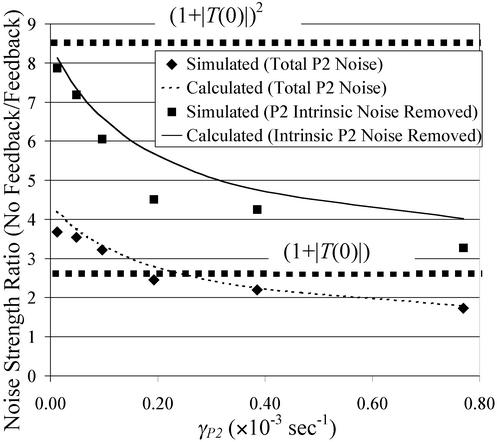
Fig 3.
Calculated and simulated ratio of p2 noise strengths (p1 circuit: without feedback (i.e., kR1 = constant)/with feedback) of the gene cascade in Fig. 2a. This ratio is plotted both for total p2 noise and with the p2 intrinsic noise removed, and shows that feedback may decrease the effect of p1 noise by as much as (1 + |T(0)|)2. The calculations were performed by using Eq. 16 for the regulated p1 noise strength and Eq. 9 for the intrinsic p2 and unregulated p1 noise strengths. The total p2 noise strength was found by adding the intrinsic p2 noise strength to the p1 noise strength multiplied by the noise power gain, (dp2/dp1)2|p1 = 〈p1〉, and modifying the noise bandwidth to reflect the additional p2 pole. The parameters for this circuit are as follows: b1 = 8, b2 = 4, γp1 = 0.0001925/s, γR1 = 0.00289/s, γR2 = 0.00578/s, kd1 = 800, kd2 = 600, krmax1 = 0.0231/s, krmax2 = 0.05/s, n1 = n2 = 7. For the no feedback case, kR1 was set to a constant value of 0.0167/s, giving the same value of 〈p1〉, 700, for both feedback and no feedback cases. 〈p2〉 varied with the value of γp2, but was the same for feedback and no feedback cases. The intrinsic noise of p2 was determined in simulation by setting kR2 = 0.0367/s whereas all other parameters remained unchanged. The simulation method is described in Appendix.