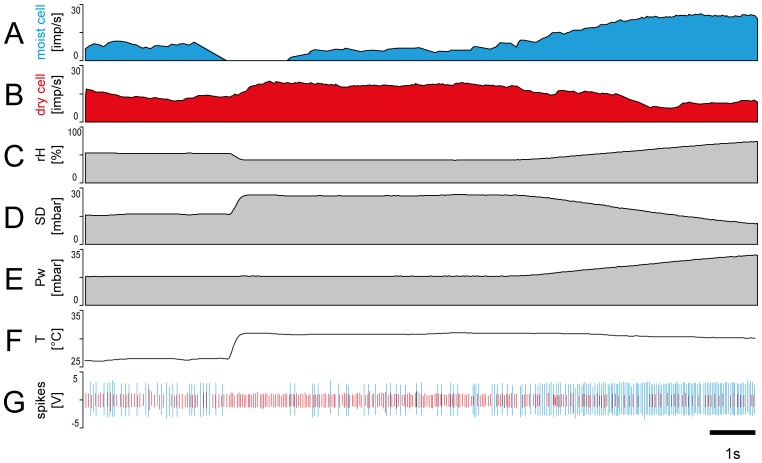
Figure 4. Simultaneously recorded responses of a pair of moist and dry cells from a single sensillum to transient and ramp-like changes in humidity.
A. and B. Antagonistic responses of moist and dry cells to humidity changes produced by an increase in temperature at constant water vapor pressure or an increase in water vapor pressure at constant temperature. Instantaneous impulse frequency; bin width, 1 s. C. Time course of relative humidity. Final 3 seconds of a 20 s presentation of an air stream with 49.5% rH, followed by a humidity drop to 37.5% rH which was held for 7 s; stimulus direction was then reversed by presenting a ramp-like humidity increase from 41.0% to 74.1% rH. D. Time course of saturation deficit. The drop in relative humidity shown in C is expressed as jump in saturation deficit from 15.9 mbar to 25.0 mbar, and the ramp as a slow decrease from 25.0 to 10.6 mbar. E. Time course of water vapor pressure. The humidity ramp was produced by changing the water vapor pressure slowly from 18.1 to 31.5 mbar. F. Time course of temperature. Rapid humidity change produced by a temperature drop from 26°C to 30°C. G. Digitized action potentials of the moist and dry cells recorded simultaneously with a single electrode and discriminated on-line. Pw water vapor pressure, rH relative humidity, SD saturation deficit, T temperature, V volt.