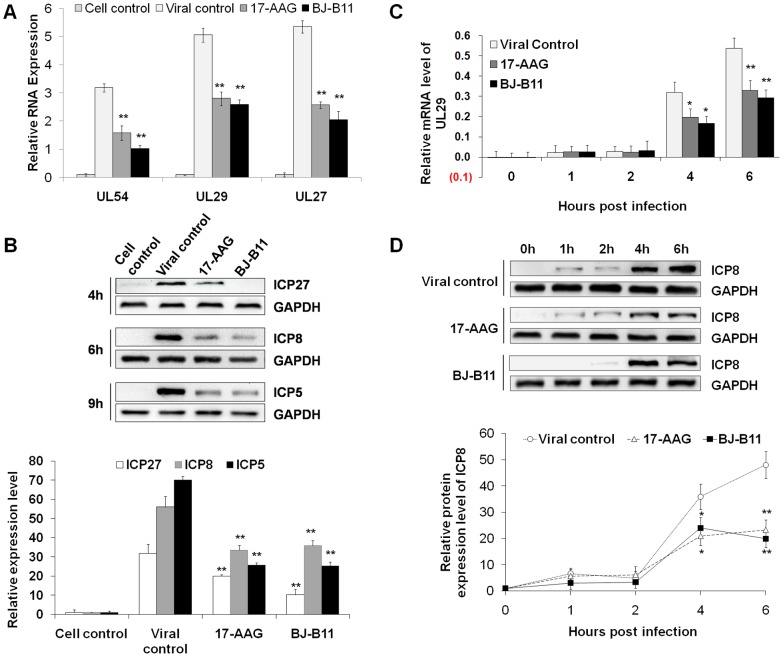
Figure 1. Hsp90 inhibitors suppress viral RNA synthesis and protein expression.
(A) Inhibition of viral RNA synthesis. MRC-5 cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI = 10) in the presence of Hsp90 inhibitor (0.8 µM). RNA samples were extracted at 4, 6, and 9 h p.i. and reverse transcribed to cDNA, which was used for UL54 (immediate early gene), UL29 (early gene), and UL27 (late gene) detection, respectively. (B) Inhibition of viral protein expression. MRC-5 cells were infected with HSV-1 (MOI = 10) in the presence of Hsp90 inhibitor (0.8 µM). Protein samples were extracted at 4, 6, and 9 h p.i. and used for ICP27 (immediate early protein), ICP8 (early protein), and ICP5 (late protein) detection, respectively. The Western blotting results shown in the bar graph were normalized to GAPDH expression and were expressed as the fold increase relative to the cell control. (C, D) Time-dependent inhibition of viral RNA synthesis or protein expression. MRC-5 cells were infected with HSV-1 for indicated times in the presence of Hsp90 inhibitor (0.8 µM). Total RNA or protein was extracted and analyzed for UL29 (C) and ICP8 expression (D). The results were expressed as the fold increase relative to the cell control. Each value represents the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (*, P<0.05; and **, P<0.01, compared with the viral control).