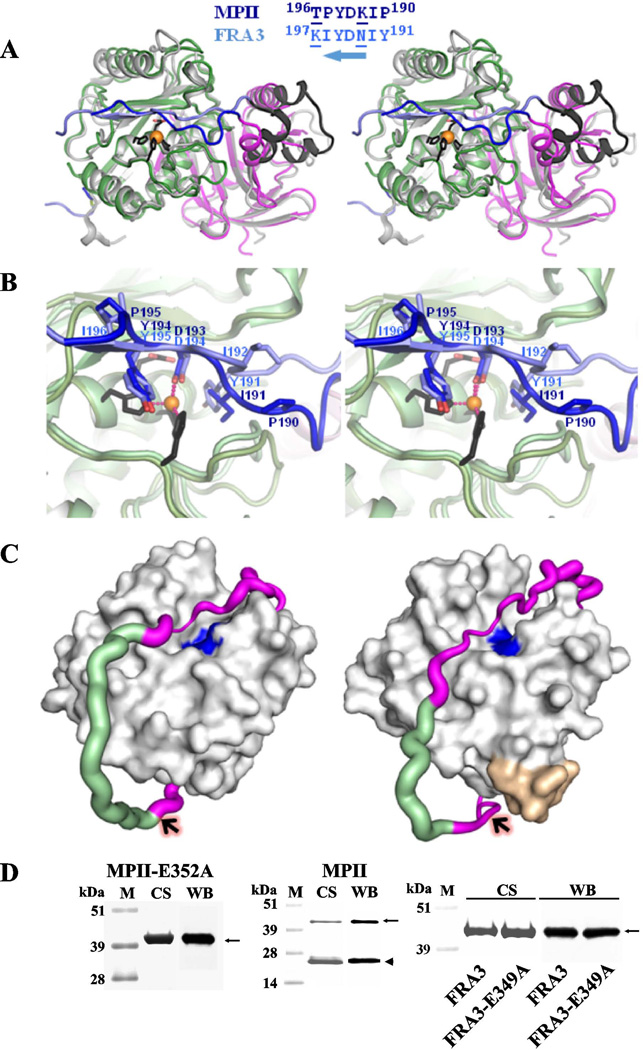
Figure 3. Structural differences between MPII and FRA3.
(A) Wall-eyed stereo view of the superimposed FRA3 and MPII structures. FRA3 is shown in grey and black. The prodomain and the catalytic domain of MPII are magenta and green, respectively, and the interdomain linker is blue. The C-terminal portion of the FRA3 prodomain is black. The active site Zn2+ ion is shown as an orange ball and the three histidines as black sticks. The alignment of the C-terminal linker is shown on the top. Substitutions of Tyr191, Asn193 and Ile196 (in FRA3) for Pro190, Lys192 and Pro195 (in MPII), respectively, result in a different fold of this linker region. Solvent-exposed residues are underlined. An arrow indicates that the prodomain runs in the antiparallel orientation in the active site relative to the substrate. (B) Wall-eyed stereo view of the active site in MPII and FRA3. The color scheme is as in A. (C) The linker is stabilized by the C-end segment of the catalytic domain in FRA3 (right) but not in MPII (left). The catalytic domain is represented as a grey surface. The active site is shown in blue. The C-terminal Glu-Ile-Ala-Asp-Gly-Asp397residue buckle (yellow) is present in FRA3, but not in MPII. The linker is shown as a magenta/green tube the width of which is proportional to the B-factor (a measure of mobility of a particular part of a protein) that varied from 20 to 80 A2. The residues with the missing electron density are modeled and colored in green. Arrows indicate the scissile bond between the linker and the catalytic domain in MPII and FRA3. (D) SDS-electrophoresis of the purified constructs. M, molecular weight markers. CS and WB, Coomassie staining and Western blotting with an anti-FLAG tag antibody, respectively. Solid arrows and arrowheads point to the proenzyme and active enzyme, respectively.