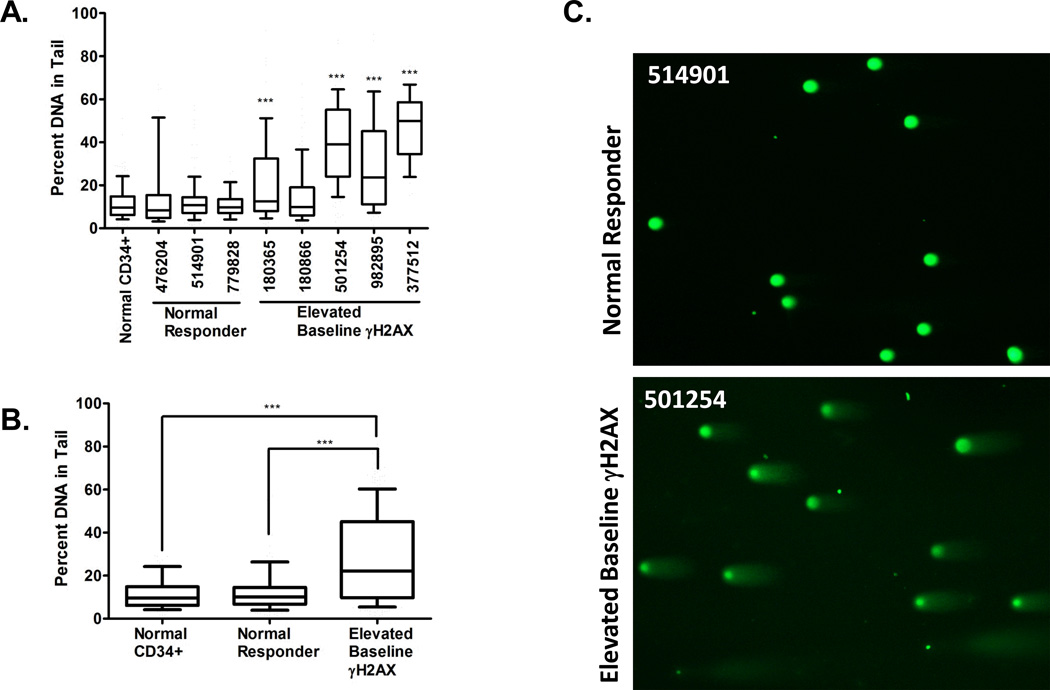
Figure 4.
Elevated double-strand breaks (DSBs) are present in bone marrow cells isolated from t-AML patients harboring gains on chromosome 8. DSB were measured in bone marrow cells by the neutral Comet assay and Comets were scored by Comet Score software. (A) Four of 5 patients with gains on chromosome 8 (UPNs 180365, 501254, 982895, and 377512) had elevated basal DSB compared to normal donor CD34+ cells, while the DSB levels in t-AML patients with normal γH2AX levels (normal t-AML responders, UPNs 476204, 514901, 779828) did not differ from CD34+ controls. Box-whisker plots were generated, with the box showing the 25th to 75th percentiles, the bar representing the median, and the whiskers representing the 10th to the 90th percentiles of the percent of DNA in the tail. The percent of DNA in the tail for CD34+ cells was compared to the percent of DNA in the tail for each UPN. The median number of Comets scored per UPN was 133 (range 44–256). (B) Comet data were pooled for the patients with normal γH2AX kinetics (n=3 patients, 317 total Comets) and those harboring gains on chromosome 8 (n=5 patients, 646 total Comets) and analyzed as above. The mean percent of DNA in the tail from t-AML with trisomy 8 (28.2%) is significantly higher than patients with normal γH2AX (13.2%) and CD34+ controls (11.8%). (C) Representative Comets from a t-AML patient with normal γH2AX kinetics (normal t-AML responder) (UPN 514901) and from a patient with trisomy 8 (UPN 501254) are shown. ***p<0.001.