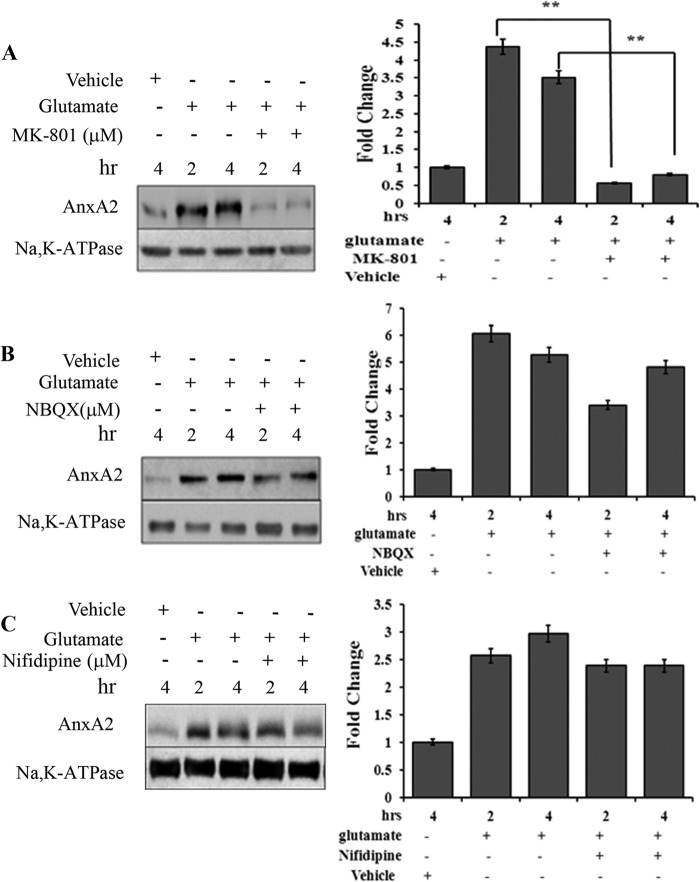
FIGURE 3.
Glutamate-induced AnxA2 cell surface translocation is NMDA receptor-mediated. A, Western blot analysis (left panel) of the cell surface biotinylated extracts from 661W cells treated for different times with MK-801 (10 μm), a NMDA receptor antagonist, in the presence of glutamate. Right panel, quantitation. **, p < 0.01. B, the effect of an inhibitor for the non-NMDA receptor, NBQX (25 μm), on glutamate-induced cell surface translocation of AnxA2 was tested in a time dependent manner. A Western blot analysis (left panel) for the cell surface biotinylated extracts is shown. Right panel, quantitation. C, Western blot analysis (left panel) for the cell surface biotinylated extract showing the effect of calcium channel blocker nifedipine on the glutamate-induced translocation of AnxA2 to the membrane in a time-dependent manner. Right panel, quantitation. Anti-Na,K-ATPase antibody served as a loading control for A–C. The fold change to the respective vehicle (dimethyl sulfoxide) control treatments is shown. For comparison, we also checked the cell surface levels of AnxA2 in untreated and glutamate-treated cells in the absence of MK-801, 2,3-dioxo-6-nitro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrobenzo[f]quinoxaline-7-sulfonamide (NBQX), and nifedipine for the indicated time. Each experiment was repeated three times (n = 3).