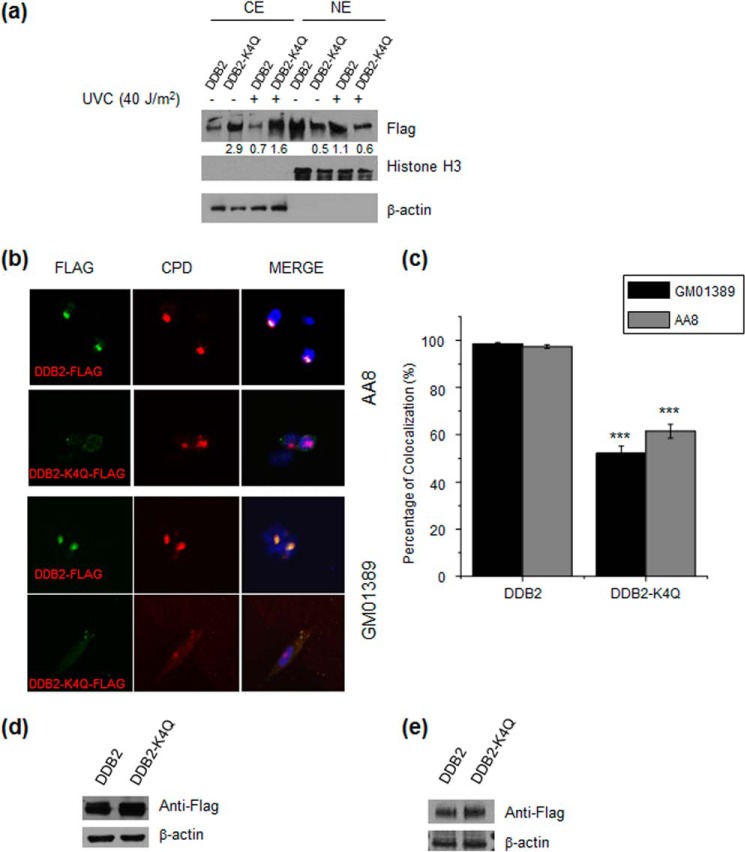
FIGURE 6.
α-N-methylation is important for the nuclear localization and recruitment of DDB2 to DNA damage foci. a, Western blot analysis revealed less nuclear localization and more cytoplasmic localization of DDB2-K4Q than wild-type DDB2 in HEK293T cells with or without exposure to UV-C light. β-actin was used as a loading control for the cytoplasmic extract (CE), and histone H3 was used as a loading control for the nuclear extract (NE). b, representative images for monitoring the colocalization of transfected wild-type DDB2 and DDB2-K4Q to CPD foci in AA8 and GM01389 cells. c, percentage of CPD foci that are colocalized with DDB2 foci. In cells transfected with the wild-type DDB2 construct, almost all CPD foci colocalization with DDB2 foci, whereas only a portion of CPD foci colocalized with DDB2 foci in cells transfected with the DDB2-K4Q plasmid. The results represent the mean ± S.E. of results obtained from three biological replicates, and ∼100 cells were counted in each replicate. ***, p < 0.001. The p values were calculated by unpaired, two-tailed Student's t test. d and e, Western blot analysis of wild-type DDB2 and DDB2-K4Q in whole-cell extracts of AA8 (d) and GM01389 (e) cells transfected with the corresponding DDB2 constructs. β-actin was used as a loading control.