FIGURE 2.
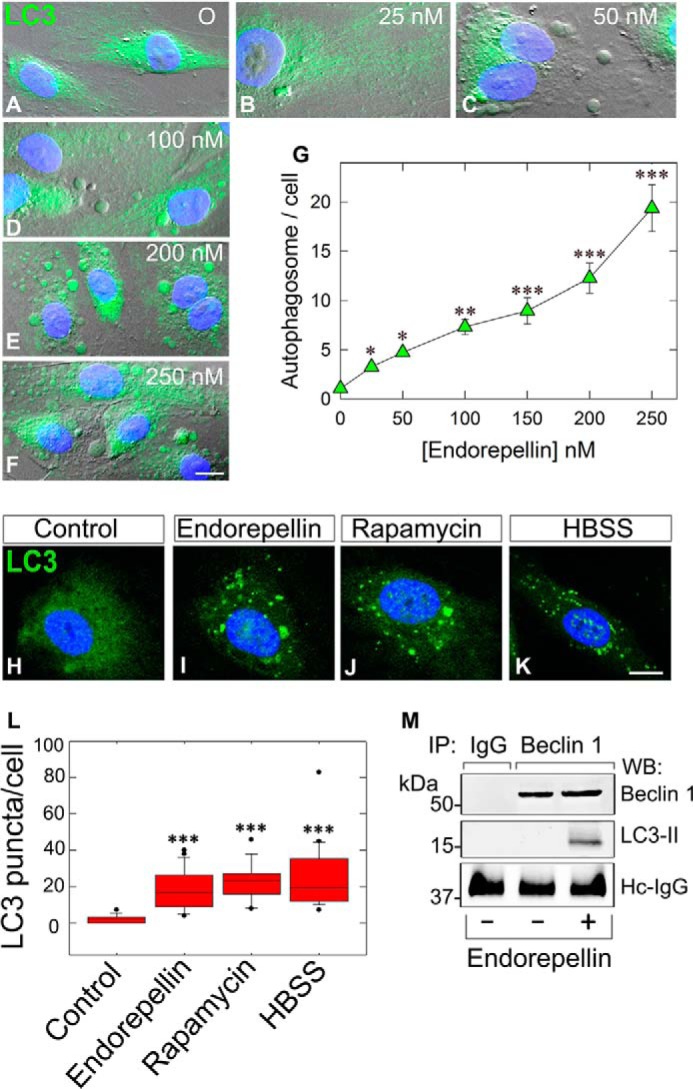
Endorepellin induces endothelial cell autophagy in a dose-dependent manner and promotes LC3-II interaction with Beclin 1. A–F, representative DIC immunofluorescence images of HUVEC exposed to the designated concentrations of endorepellin for 6 h. Notice the progressive formation of autophagic vesicles labeled by anti-LC3 antibody (green) and counterstained with DAPI (blue nuclei). Bar, 10 μm. G, quantification of autophagosomes/HUVEC from three independent experiments. Data represent mean ± S.E. from 52–75 cells/experimental condition; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. H–K, representative confocal images of HUVEC treated with endorepellin (200 nm), rapamycin (40 nm), or HBSS for 6 h showing increased expression of LC3 (green) and its relocalization to autophagosomes. L, quantification of the number of LC3-containing vacuoles per cell showing a significant increase in the amount of LC3-positive vacuoles upon treatment. Means ± S.E. (n = 3); ***, p < 0.001. M, representative co-immunoprecipitation of HUVEC stimulated with endorepellin (200 nm) for 6 h. The cells were lysed, immunoprecipitated (IP) with an anti-Beclin 1 antibody, and subjected to Western blot (WB) with anti-Beclin 1 and anti-LC3 as indicated. Nonspecific IgG served as negative control. The experiments were repeated three times with comparable results. Hc-IgG, heavy chain IgG.
