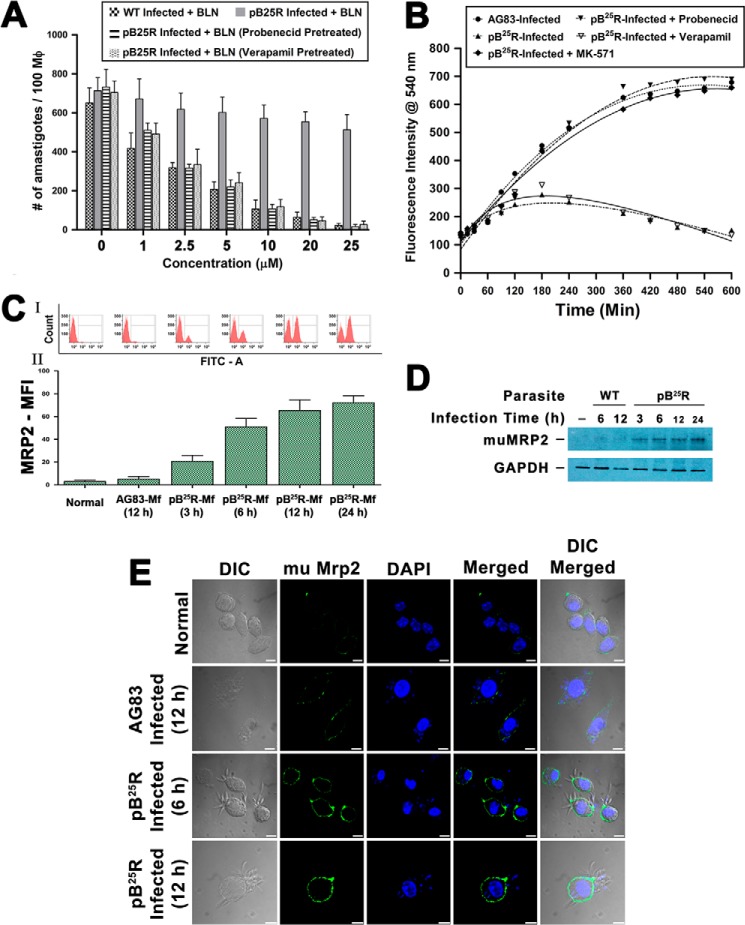
FIGURE 5.
A, effectiveness of clearance of internalized wild type L. donovani (AG83) and resistant L. donovani pB25R infection by baicalein from in vitro infected mouse Mf. Macrophages from peritoneal exudate of a Balb/c mouse were infected either with wild type AG83 or BLN-resistant pB25R parasites. Twenty-four hours postinfection, cultures were treated with BLN as indicated under “Experimental Procedures.” Incubations were carried out for 24 h. Cells were fixed, stained with Giemsa, and counted under a bright field microscope. For pB25R parasitic infection, probenecid and MK571 pretreatment were performed followed by baicalein treatment. Results shown are the means of three independent experiments and are plotted as mean ± S.D. ***, p < 0.001 compared with 1 μm inhibitor treatment. B, accumulation of BLN in macrophages infected either with wild type or BLN-resistant parasites. Intracellular total BLN content was measured by fluorescence spectroscopy. Baicalein at a concentration of 25 μm was added to macrophages after infection for 24 h with wild type AG83 or pB25R parasites. Baicalein accumulation was measured up to 10 h of incubation. To confirm the role of ABC transporters, pretreatment with probenecid, verapamil, or MK571 was followed by incubation with BLN. The fitted lines (sigmoidal) from these data points (n = 3) have R2 values of 0.9904, 0.8243, 0. 9126, 0.8947, and 0.8843, respectively. C, flow cytometry analysis of Mf-MRP2 in infected cells. Macrophages from peritoneal exudates were cultured, and then the cells were left uninfected or infected with either WT AG83 parasites or pB25R parasites for the indicated time (hours). Cells were then isolated, stained with anti-mouse MRP2 antibody, and counterstained with FITC. The cells were analyzed in a BD FACSAria II cytometer. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity. D, Western blot analysis of MRP2 level in infected macrophages. Equal numbers of cells were left uninfected or infected with either WT AG83 or pB25R parasites for the indicated time (hours). Cells were isolated and lysed as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Total cell proteins (25 μg) were separated on a 7.5% polyacrylamide gel, and immunochemical analysis was performed using anti-MRP2 antibody. As loading controls, cytoplasmic extracts were probed for GAPDH. E, confocal images of macrophage MRP2 expression after pB25R infection. Macrophages from peritoneal exudate of Balb/c mice were infected either with wild type AG83 or BLN-resistant pB25R parasites. After 6 or 12 h of infection, the excess parasites were washed off, and anti-mouse MRP2 antibody was used to probe the status of MRP2 expression on the cell surface. pB25R-Mf show up-regulated MRP2 as early as 6 h postinfection, and MRP2 increases up to 12 h of infection. Scale bars, 10 μm. Error bars represent S.D. mu, murine; DIC, differential interference contrast.