FIGURE 3.
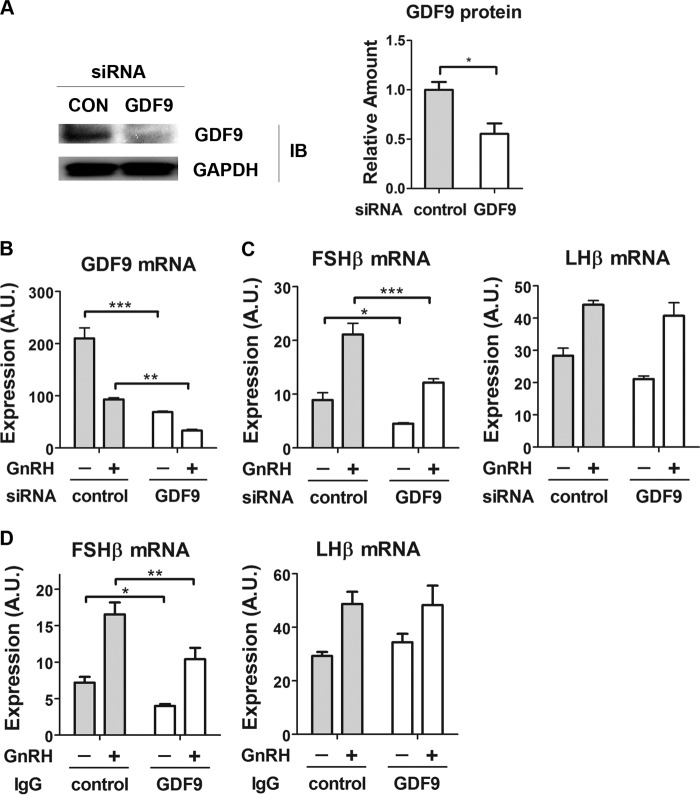
Effect of GDF9 inactivation on gonadotropin subunit gene expression. A, knockdown efficiency of GDF9 siRNA at the protein level. Left, 2 days after transfection, LβT2 whole cell lysates were subjected to a quantitative Western blot analysis using GDF9-specific antibodies. Right, Western blot densitometry was quantified from three independent experiments and plotted as mean ± S.E. (error bars). Two-tailed Student's t test was used; n = 3. *, p < 0.05. B, knockdown efficiency of GDF9 siRNA at the mRNA level. B and C, cells were transfected with either scrambled (control) or GDF9 siRNA on day 1. On day 2, cells were serum-starved overnight. On day 3, cells were stimulated with 1 nm GnRH for 2 h, followed by 4 h without GnRH, or with vehicle. D, cells were serum-starved overnight and treated with either 2 μg of control antibody (IgG) or 2 μg of GDF9 IgG for 8 h. After the first 2 h of antibody treatment, cells were exposed to vehicle or to 1 nm GnRH for 2 h, followed by 4 h without GnRH. GDF9, FSHβ, and LHβ mRNA expression levels were determined by qPCR. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test corrections was used. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments. A.U., arbitrary units.