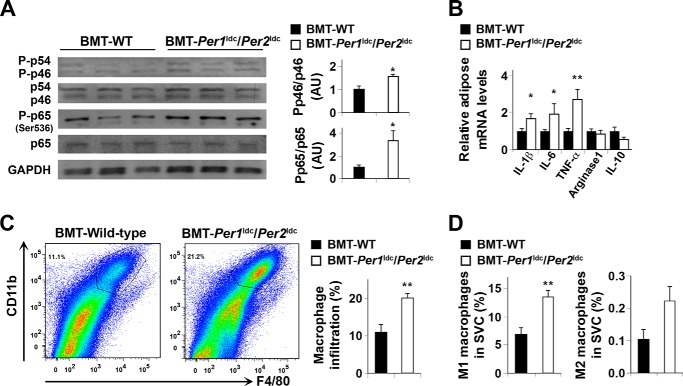
FIGURE 6.
Myeloid cell-specific Per1/2 disruption exacerbates HFD-induced adipose tissue inflammation. Chimeric mice (BMT-WT and BMT-Per1ldc/Per2ldc) were fed an HFD for 12 weeks (n = 6–10). Before tissue collection, mice were fasted for 4 h starting at the same time of the day. A, adipose tissue inflammatory signaling. The levels of total and phosphorylated JNK1 (p46) and NF-κB p65 were examined using Western blot analyses and quantified using densitometry. B, adipose tissue expression of genes related to macrophage polarization. The mRNA levels of cytokines and arginase1 were quantified using real-time PCR and plotted as relative expression. C, FACS analyses of macrophage infiltration in epididymal fat pads of HFD-fed chimeric mice. Left two panels, representative plots of adipose tissue SVC that were quantified for F4/80 and CD11b expression; right panel, percentages of mature macrophages (F4/80+ CD11b+ cells). D, quantification of proinflammatory (M1) macrophages (F4/80+ CD11b+ CD11c+ CD206− cells), and anti-inflammatory (M2) macrophages (F4/80+ CD11b+ CD11c− CD206+ cells) in SVC isolated from adipose tissue of HFD-fed chimeric mice. For bar graphs (A–D), data are the means ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 BMT-Per1ldc/Per2ldc versus BMT-WT (A, C, and D) for the same gene (B). AU, arbitrary units.