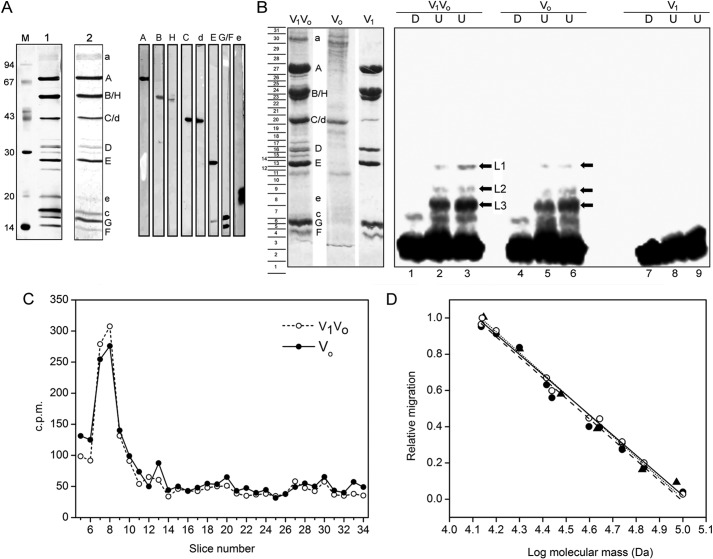
FIGURE 4.
Characterization of PA1b binding. A, left, SDS-PAGE analysis of purified M. sexta V-ATPase with staining with silver (lane 1) or Coomassie Brilliant Blue (lane 2) and M indicating molecular mass markers. Right, identification of the staining polypeptides by immunoblot analysis. B, photoaffinity labeling of M. sexta V-ATPase with the 125I-PA1b-benzophenone. For labeling, V1Vo holoenzyme (V1Vo), Vo complex (Vo), or V1 complex (V1) was incubated with 125I-PA1b-benzophenone and exposed to UV light or kept in the dark. After separation by SDS-PAGE, the stained and dried gel was exposed to a phosphorimaging screen. Left, SDS-PAGE of the V-ATPase complexes with Coomassie Blue staining. Right, readout of the phosphorimaging screen for labeled holoenzyme (lanes 1–3), Vo (lanes 4–6), and V1 (lanes 7–9) after either UV irradiation (U) or maintenance in the dark (D). Bands L1–L3 (arrows) indicate UV-dependent labeled species. C, slices of the dried gel from samples of the V1VO holoenzyme (open circles) and Vo (filled circles) subjected to scintillation counting. The column to the left of B indicates positions of gel slices subjected to counting. The majority of the radioactivity was found in slice 3 near the dye front. D, molecular mass determination of 125I-labeled V-ATPase subunits. A calibration curve was prepared by plotting log molecular masses of standard proteins (triangles, dashed line) and V-ATPase subunits (deduced from their primary structure) against their relative migration on the SDS-polyacrylamide gels shown in A (open circles, dotted line) and B (filled circles, solid line). In each case, linear regression gave r2>0.99.