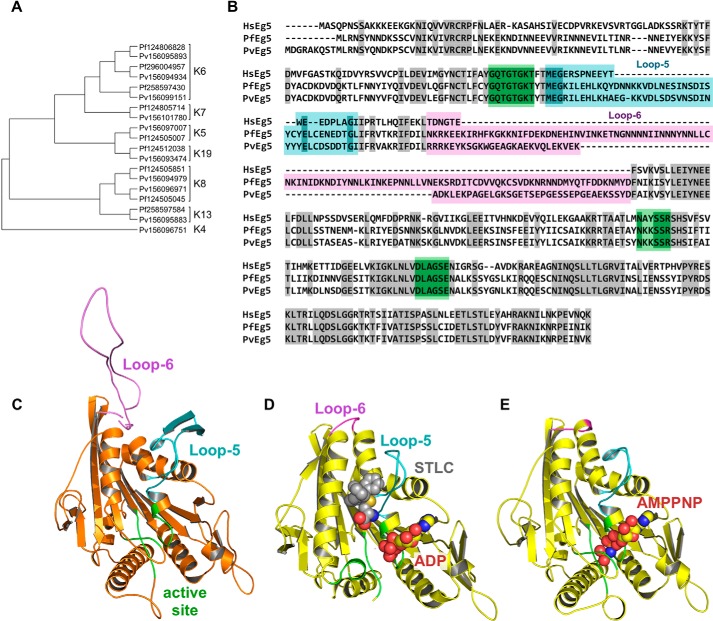
FIGURE 1.
Identification of P. falciparum and P. vivax kinesins. A, left, unrooted, SATé phylogenetic tree of all kinesins in P. falciparum and P. vivax. Sequences are identified as P. falciparum (Pf) or (Pf) or P. vivax (Pv), followed by genbank GI number. Brackets indicate kinesin family affiliation (K number) of each sequence. B, sequence alignment of the motor domains for HsEg5, PvEg5, and PfEg5. Identical residues are shaded gray. Loop-5 and loop-6 segments are marked and shaded in cyan and magenta, respectively, whereas the orthosteric site residues are shaded in green. The Plasmodium motor domains are ≤45% identical to the HsEg5 motor domain, whereas their orthosteric sites are 90% identical to HsEg5. C, homology model of PvEg5 based on the 3HQD structural template (36) with loop-5, loop-6, and the orthosteric site colored as in B. D, x-ray structure of HsEg5 motor domain co-crystalized (3KEN) (34) with inhibitor (gray space-filling representation, S-trityl-l-cysteine), loop-5 (cyan), loop-6 (magenta), and ADP (yellow/red space-filling representation) to illustrate the allosteric loop-5 pocket. E, x-ray structure of HsEg5 (3HQD), colored as in D, with bound AMPPNP (space-filling representation) trapped in a prehydrolysis state.