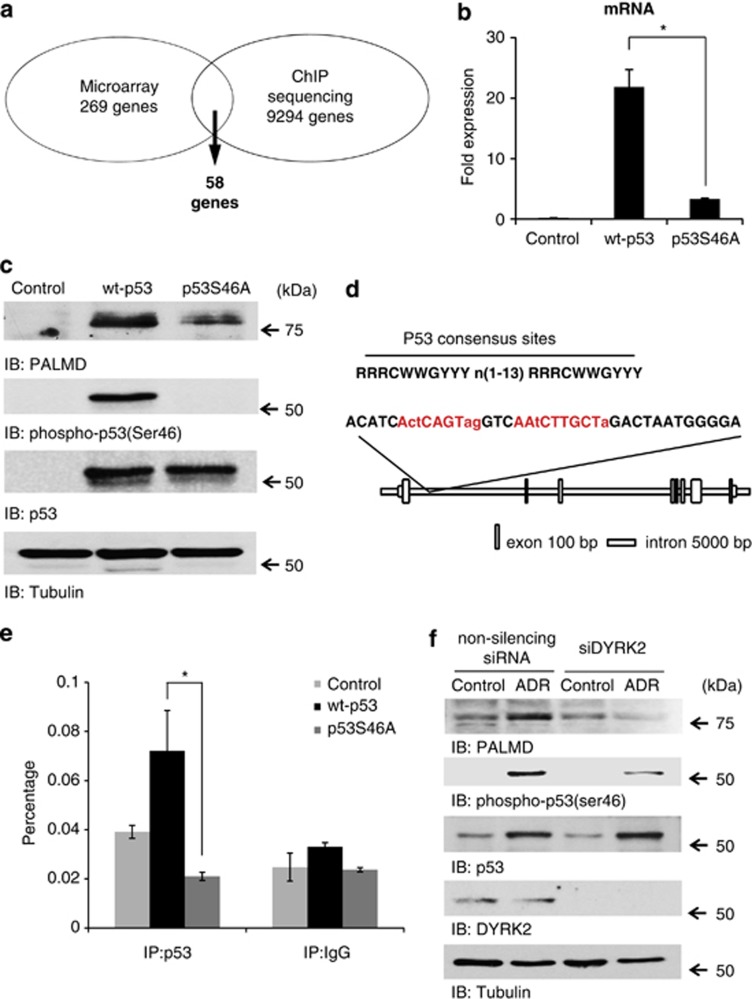
Figure 1.
PALMD is induced by p53 when ser46 is phosphorylated. (a) A genome-wide search of the pro-apoptotic genes promoted by phosphorylated p53 at ser46. Results of microarray and ChIP sequencing were overlapped to identify novel targets of phospho-ser46 of p53. (b) Control vector (control), wild-type p53 (wt-p53), and mutant p53 at serine-46 (p53S46A) were transfected into SaOS2 cells. Real-time PCR was performed and data represents fold change in PALMD relative to the GAPDH. *P<0.01. (c) Samples described in b were analyzed by western blotting. Protein-specific bands were detected with anti-PALMD (top panel), anti-phospho-p53(Ser46) (second panel), anti-p53 (third panel), or anti-tubulin (bottom panel). (d) The highest peak region of PALMD by ChIP sequencing that includes p53 consensus sites (red color). This region was amplified in the ChIP assay. (e) The binding of p53 onto PALMD was identified by the ChIP assay. Cell lysates from samples described in b were immunoprecipitated with anti-p53 or anti-immunoglobulin (Ig)G. ChIP assay and subsequent real-time PCR were performed. The data were normalized with the level of input control. *P<0.01. (f) DYRK2-depleted cells failed to induce PALMD expression. U2OS cells were transfected with non-silencing siRNA or siDYRK2. Cells were treated with ADR or left untreated. Cell lysates were immune-stained with anti-PALMD, anti-phospho-p53(Ser46), anti-p53, anti-DYRK2, or anti-tubulin