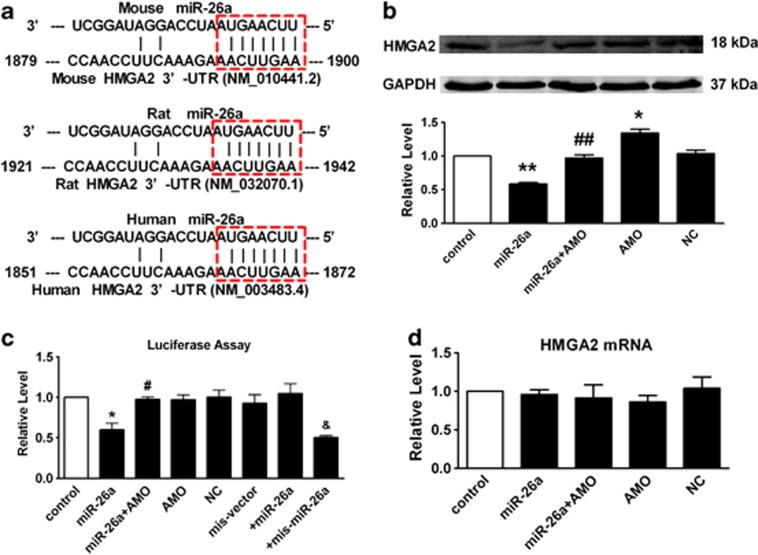
Figure 4.
miR-26a post-transcriptionally regulates HMGA2. (a) Sequence alignment showing miR-26a/HMGA2 complementarity for mouse, rat and human genes. The matched base pairs are outlined by dashed red rectangles. The Genbank accession numbers of the genes are indicated in the brackets, and the positions of the target sites are numbered. (b) Compared with control, transfection of miR-26a results in a significant decrease of HMGA2. Co-application of miR-26a with AMO-26a alleviated the reduction of HMGA2, whereas NC showed no effects. (c) Compared with control, transfection of miR-26a with the luciferase reporter gene vector containing the wild-type 3′ UTR of HMGA2 results in a significant decrease of luciferase activity. Co-application of miR-26a with AMO-26a alleviated the reduction of luciferase activity, whereas NC showed no effects. (d) Real-time PCR shows that miR-26a had no effects on HMGA2 mRNA level. AMO/miR-26a inhibitor, AMO-26a; NC/negative control. Mean±S.E.M.; n=4 represents three independent experiment under each condition; *P<0.05, **P<0.01 versus control; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 versus miR-26a, &P<0.05 versus mis-vector