Figure 5.
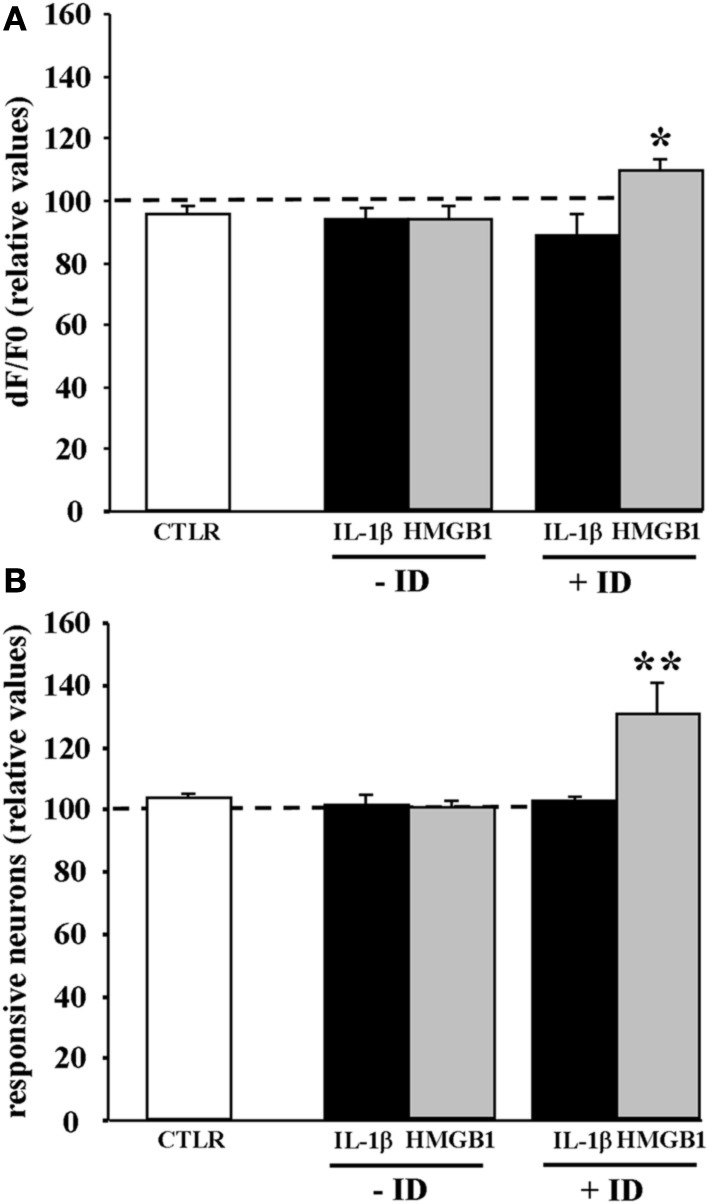
HMGB1 can act directly onto NMDA receptors after the brain tissue experienced epileptiform activities. Mean peak amplitude of the neuronal Ca2+ change (A) and mean number of responsive neurons (B) evoked by a single NMDA pulse applied in 0.5 mM Mg2+ and TTX. Slices were treated with IL1β or HMGB1 and experienced (+ID) or did not experience (−ID) an ictal-like discharge before TTX application. IL1β (black bars; 12 slices, 465 neurons, 9 animals), HMGB1 (gray bars; 13 slices, 575 neurons, 9 animals). The white bars correspond to data from control slices with saline applications instead of the cytokine applications (6 slices, 290 neurons, 3 animals). In each experiment Δ F/F0 max values and number of NMDA responsive neurons after cytokine treatment are normalized with respect to internal control. Neurons from the HMGB1 treated slices that experienced previous epileptic activity increase significantly their response to NMDA (7 slices, 5 animals). *p = 0.05, **p = 0.01, Mann-Whitney test.
