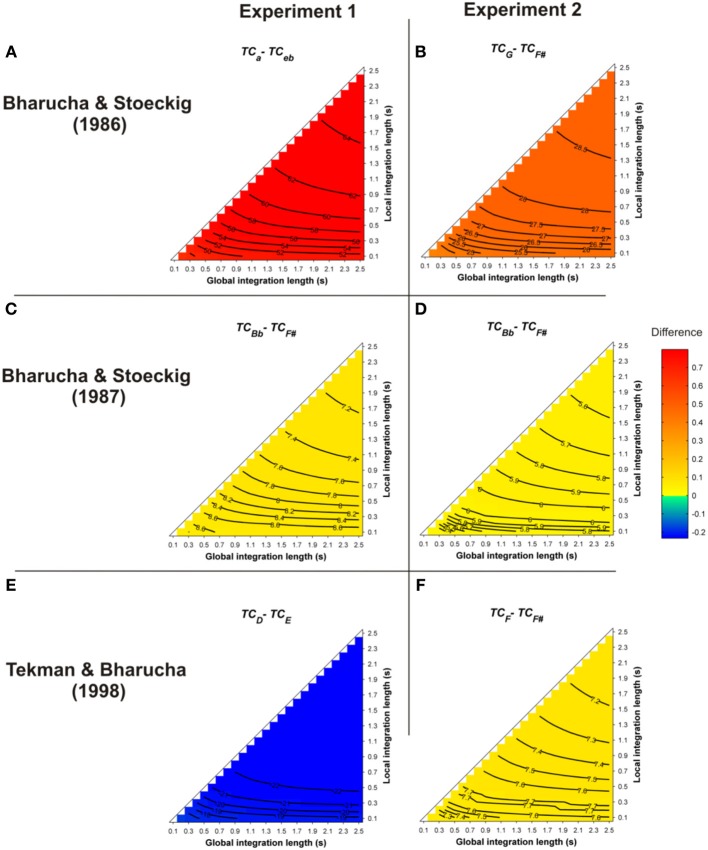
Figure 2.
Mean differences between the TC of the target chords (TCrelated − TCunrelated), following a single-prime chord, as a function of the local and global context integration windows. Rows indicate different studies (Panels A,B: Bharucha and Stoeckig, 1986; Panels C,D: Bharucha and Stoeckig, 1987; Panels E,F: Tekman and Bharucha, 1998). Positive, negative, and nonsignificant differences are represented by hot, cold, and white colors, respectively (two-tailed paired t-test, p < 0.05; t-values are reported as contours). A positive difference indicates that the TC in ASTM induced by the related target is stronger than that of the unrelated one, thus predicting the harmonic priming effects reported in the behavioral studies. For five out of six experiments, the ASTM model predicted the observed facilitation for the related target over the unrelated target, as reflected by hot colored areas. The targets chords in each experiment are indicated by the indices (lowercase and uppercase letters represent minor and major chords, respectively).