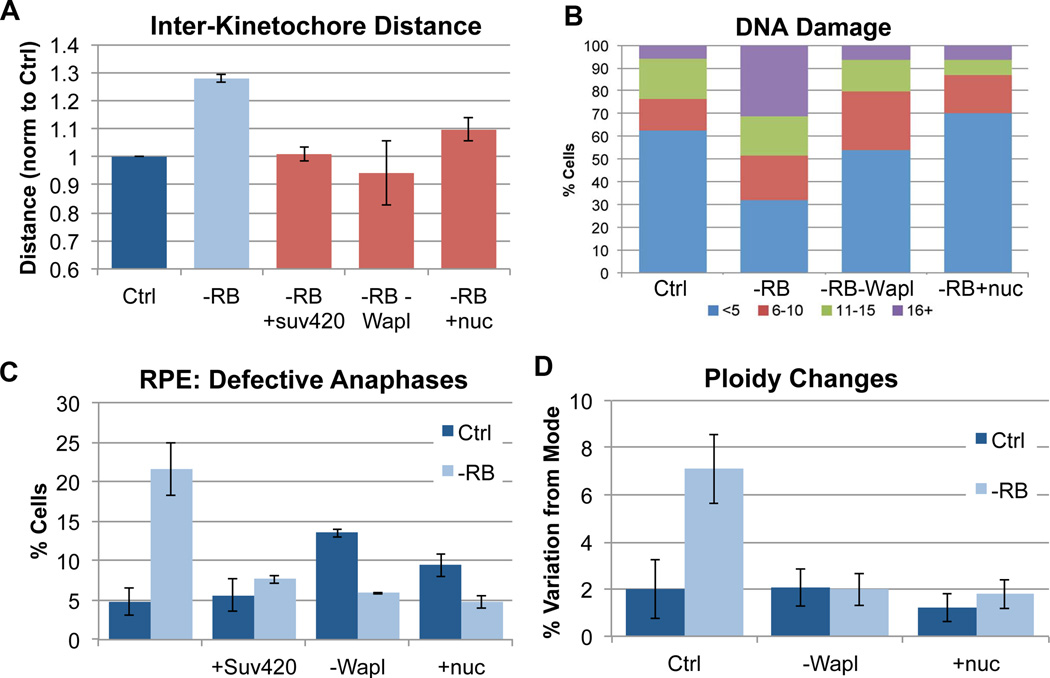
Figure 5. Promoting cohesion in pRB-depleted cells suppresses defects associated with genome instability.
A) The distance between paired sister kinetochores in mitotic cells (marked with ACA & Hec1 antibody) was measured as a readout of functional mitotic cohesion. Overexpression of Suv4-20, co-depletion of Wapl, and nucleoside addition all similarly suppressed centromeric cohesion defects during mitosis in pRB-depleted cells. B) Using γH2AX foci as a readout, pRB depleted cells were seen to exhibit increased DNA damage. Both co-depletion of Wapl and nucleoside addition suppressed the frequency and extent of γH2AX foci. The percent of cells with <5 foci (blue), 6–10 foci (red), 11–15 foci (green), and 16 or more foci (purple) is indicated for each condition. C) Immunofluorescence analysis of DAPI, α-tubulin and ACA staining demonstrate that the presence of lagging chromosomes during anaphase following pRB depletion was significantly decreased by overexpression of Suv4-20, co-depletion of Wapl and nucleoside addition. D) Variation in chromosome copy number determined using FISH analysis indicates that 36 hours after siRNA treatment, pRB-depleted cells exhibit a nearly four-fold increase in cells deviating from the modal copy number (mode = 2 in RPE cells) for each of 3 chromosomes scored. Co-depletion of Wapl and nucleoside addition suppressed the generation of aneuploid cells. See also Figure S6.