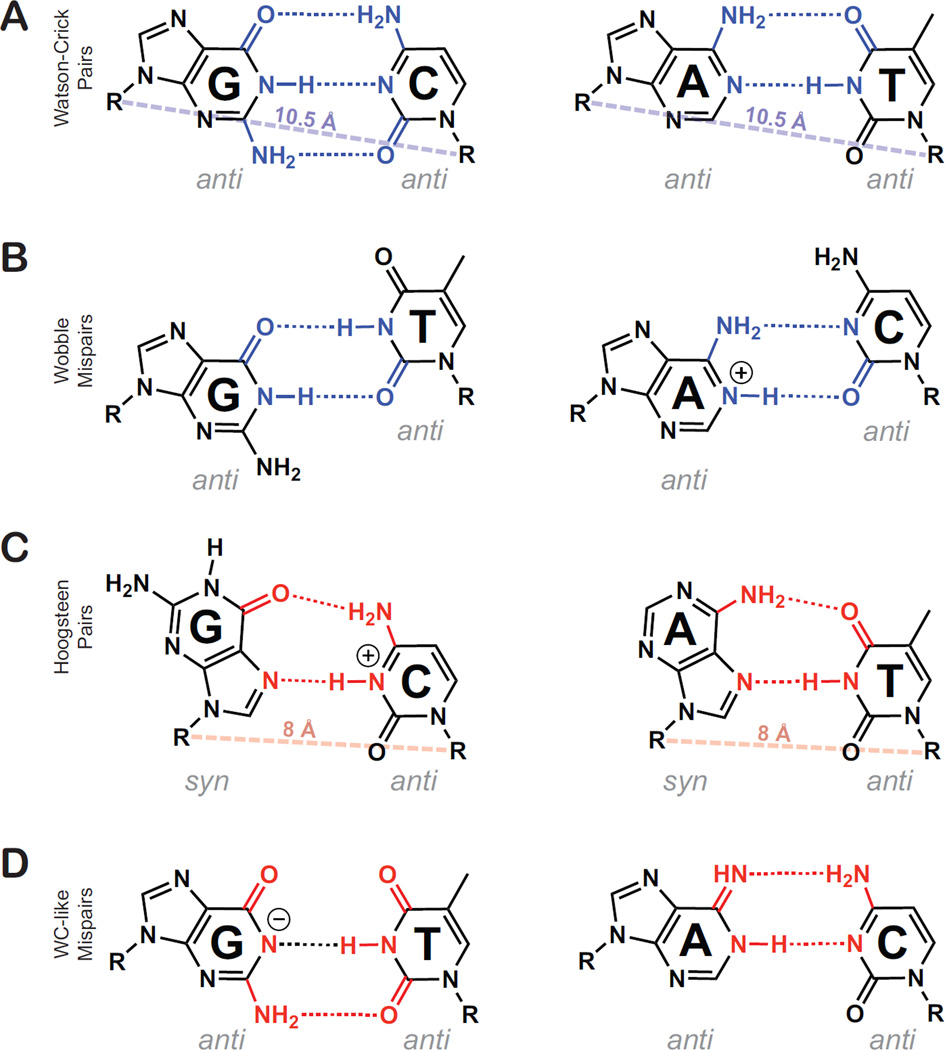
Figure 1.
Low and high energy pur-pyr pairing schemes. Hydrogen bonding partners for low energy WC and WB pairs are shaded blue, while high energy HG and WC-like mispairs’ hydrogen bonding partners are shaded red. (A) Canonical Watson-Crick G•C and A•T pairs. A rough average WC C1′–C1′ distance is shown as a dashed blue line for comparison with Hoogsteen pairs. (B) Neutral G•T wobble and ionized A+•C wobble. (C) G•C+ and A•T Hoogsteen pairing geometry, where purines are shown in the syn conformation. A rough average HG C1′–C1′ distance is shown as a dashed red line, reflecting the constriction of the C1′–C1′ distance by ~2.5 Å. (D) Deprotonated guanine in a WC-like G•T mispair is shown alongside an imino adenosine in a WC-like A•C mispair. While different tautomers and ionization states can explain the WC-like geometry, only two were shown for brevity. Possible ionized & tautomeric states that can explain the WC-like geometry for G•T mispairs include: G(enol), T(enol), G(N1-) and T(N3-). For A•C mispairs they include: A(Imino) and C(Imino).