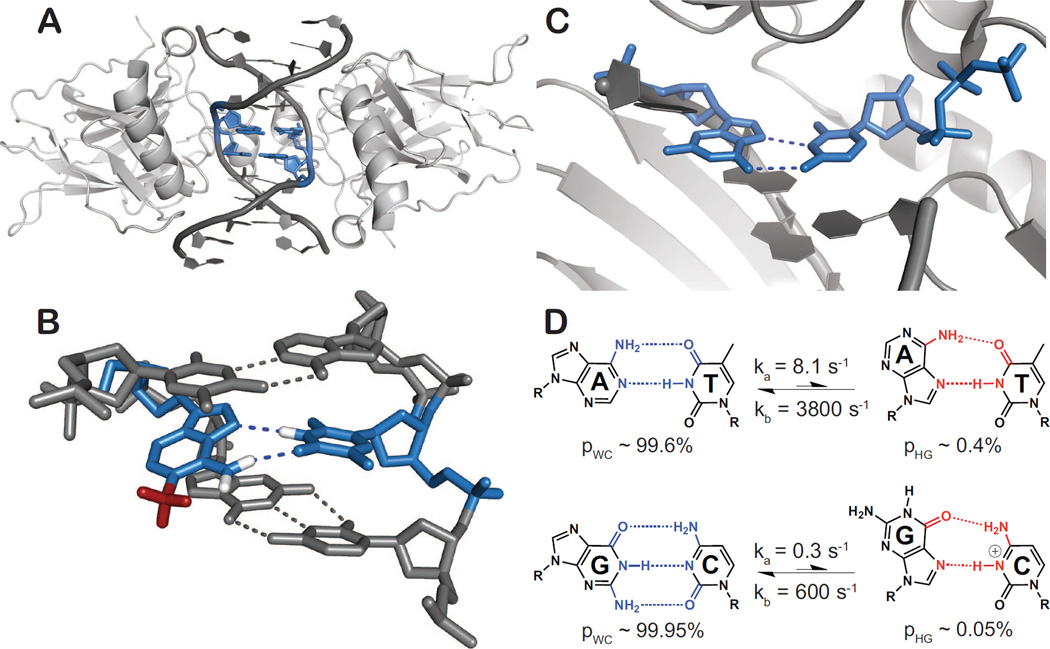
Figure 3.
Occurrence and functional roles for Hoogsteen base-pairs. A•T and G•C+ HG base-pairs are highlighted in blue. (A) Structure of DNA in complex with the p53 tumor suppressor protein provides a representative example of a DNA-protein complex containing HG base-pairs (PDB ID: 3IGL). (B) X-ray structure showing that the common DNA damaged purine, N1-methyladenine, prohibits the traditional A•T WC pairing by a steric clash of the N1-methyl group (red), and instead stabilizes Hoogsteen base-pairing with T. Protons were added to A(N1-methyl), A(N6) and T(N1) for illustrative purposes. (PDB ID: 3H8O). (C) Replication via human lesion bypass DNA polymerase ι (hPolι) proceeds through Hoogsteen (HG) base-pairing. hPolι is shown poised to insert an incoming dCTP against the template G via HG base-pair geometry (PDB ID: 2ALZ). (D) Two state conformational exchange between WC and transient HG A•T and G•C+ base-pairs in canonical duplex DNA showing the relative populations and exchange rate constants obtained from R1ρ; NMR relaxation dispersion experiments at pH 6.8 [18••,45•].