Figure 1.
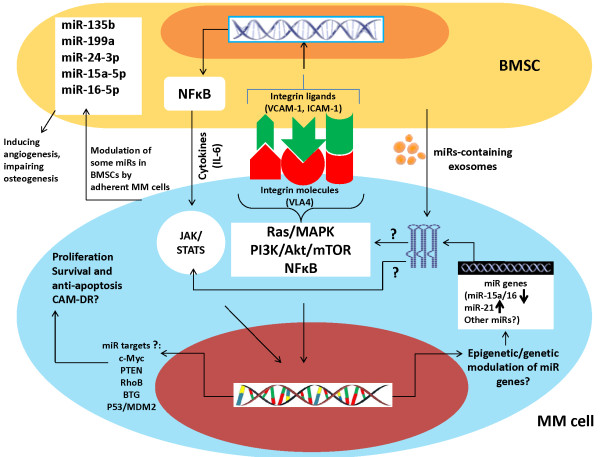
Postulated schematic model indicating how BMSCs might influence expression and function of miRs in MM cells. Following adhesion, integrin-mediated signaling in MM cells triggers activation of various pathways (mostly NFB, PI3K/Akt/mTOR, and Ras/MAPK). It is still not known whether miRs associate with these pathways, whether modulation of miR gene expression occurs through these pathways, and whether they induce some epigenetic mechanisms controlling expression of miRs. It has also been shown that BMSCs can transfer miR-containing (15a) exosomes into MM cells to induce cell growth and proliferation. IL-6 has also been demonstrated to mediate miR-15a suppression in MM cells following adhesion to BMSCs, but how this cytokine triggers such a response is not clear. Moreover, targets reported for some miRs (miR-21) in MM cells, were not explored in BMME context, hence the potential targets of miRs in MM cells adhered to BMSCs are not well characterized yet nor is there any information showing how these targets are affected by a putative integrin-miR axis. To identify potential targets of miRs in MM cell-BMSC interaction, further exploration is required. Additionally, adhesion of MM cells to BMSCs has been shown to modulate some miRs in BMSCs, leading to other disease-related complications such as angiogenesis and defective osteogenesis. However, to identify potential targets of miRs in MM cell-BMSC interaction, further exploration is required.
