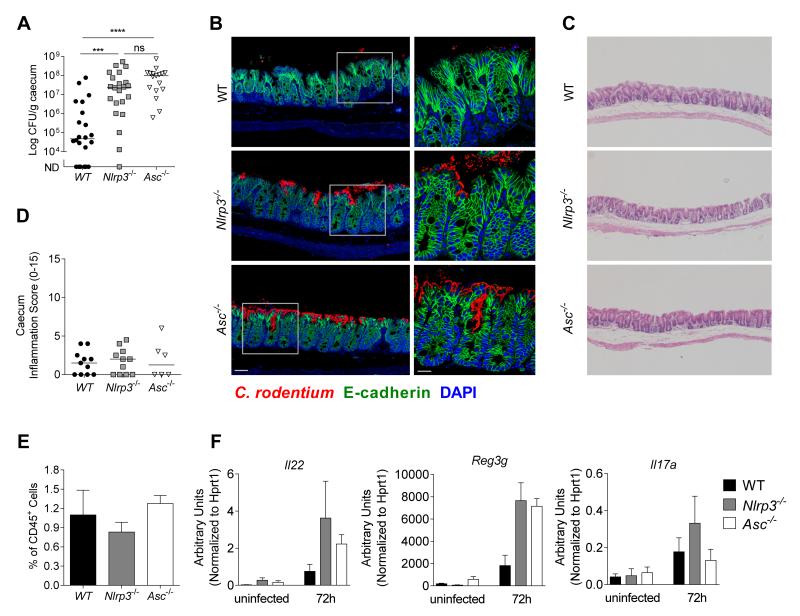
Figure 6. Nlrp3 and Asc activation mediates early control against C. rodentium.
Cohorts of WT, Nlrp3−/−, and Asc−/− mice were infected with ~109 C. rodentium and sacrificed 72hours p.i.
(A) C. rodentium loads in the caecum at 72h p.i. (n = 17-20)
(B) Caecal tissues from infected mice (72h p.i.) were stained for C. rodentium (red), E-cadherin (green) and DAPI (blue). Bar = left panel 20μm, right panel 10μm.
(C) Representative photomicrographs depicting H&E staining of C. rodentium infected caeca (magnification x50)
(D) Inflammation scores in the caecum at 72h p.i. (n = 6-11)
(E) Frequency of CD45+ Lin− Thy1+ Sca1+ innate lymphoid cells (ILC) of total CD45+ cells in the caecum at 72h p.i. (n = 4)
(F) mRNA expression levels of Il22, Reg3g, and Il17a at uninfected or 72h p.i. (n = 3)
Data obtained from two independent experiments. Bar graphs (E and F) shown are means (±SEM). Horizontal bars (A, D) represent the medians. Statistical significance was determined by the Mann-Whitney test (* = P < 0.05: ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001, **** = P < 0.0001)