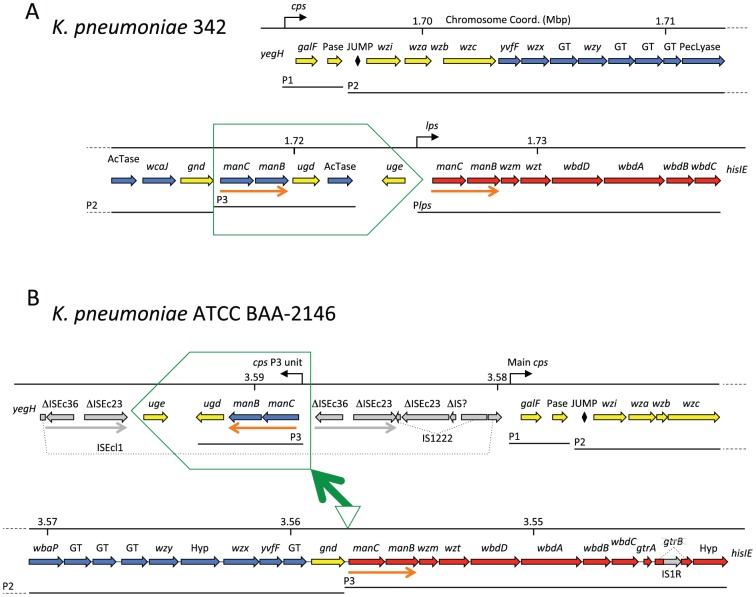
Figure 6. Operon translocation and fusion at the cps-lps polysaccharide synthesis locus.
The cps P1, P2 and P3 promoters are taken from [68], while a promoter (Plps) has been mapped in K. pneumoniae MGH 78578 to the intergenic space between uge and the first lps gene [69]. A) The cps-lps region of K. pneumoniae 342, which is typical of Klebsiella. Genes of cps are in yellow (common in most strains) or blue (varying in gene identity, count, and order); genes of lps are in red. The manCB unit (orange arrows) is occasionally found in cps, and occasionally in lps, and here unusually in both. The diamond represents the JUMPstart DNA/RNA motif at whose ops sequence RfaH is loaded onto the elongating RNA polymerase in place of NusG, preventing Rho-based termination for the small number of long transcription units that are controlled by ops-RfaH, and physically coupling the elongating RNA polymerase to the trailing ribosome [70]. B) Kpn2146 cps-lps. The boxed cps P3 unit has been deleted from its usual site, and moreover translocated to a nearby position, apparently by transposition and/or homologous recombination mechanisms; note the complex pattern of surrounding IS insertions and the directly repeated flanking sequence copies (gray arrows).ΔIS, incomplete IS copy; dotted lines, gene or IS interrupted by ISs; GT, glucosyl transferase, Hyp, hypothetical.