Figure 4.
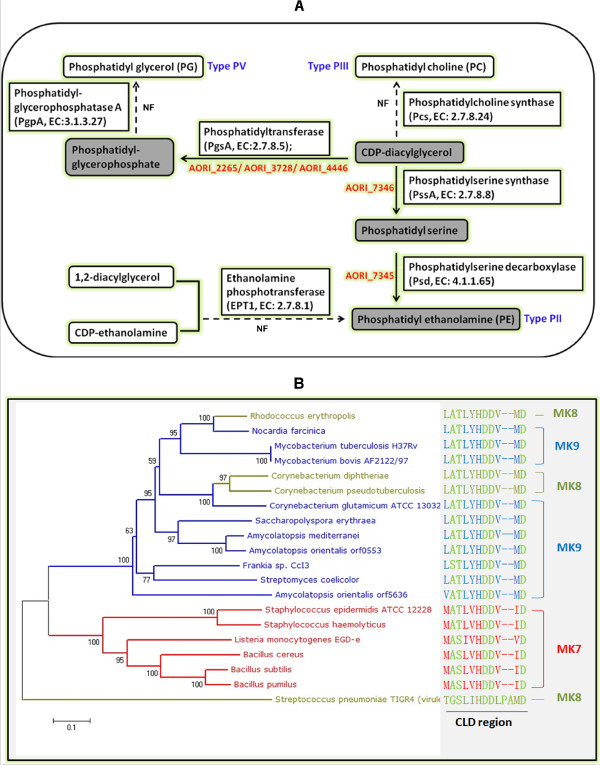
Biosynthetic pathways of different types of nitrogenous phospholipids in actinomycetes. (A) The cell membrane of Amycolatopsis belongs to the type PII because PE is the dominant phospholipid detected. Two essential proteins (AORI_7345 and AORI_7346, labeled in red color) involved in the biosynthesis of PE were encoded by the A. orientalis genome, whereas the genes encoding enzymes involved in other types of nitrogenous phospholipids were not found (NF). Actinomycetes of type PI contain no nitrogenous phospholipids in their cell membrane, while type PII, type PIII, type PIV, and type PV actinomycetes contain the following characteristic phospholipids: PE, PC, GluNU, and PG, respectively. Panel (B) illustrates the analysis of isoprenyl diphosphate synthases from type strains of actinomycetes. The names and amino-acid sequences of the strains with different colors represent actinomycetes harboring different-length MKs: red, MK7 (C35); olive-green, MK8 (C40); blue, MK9 (C45). The amino-acid sequences of the chain-length determination (CLD) region are emphasized in green on the right of the panel. The protein sequences were obtained from NCBI at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/.
