Figure S4.
Both the Short and Long Form of KDM2B Mediate Polycomb Domain Formation in a Histone Demethylase Activity-Independent Manner, Related to Figure 5
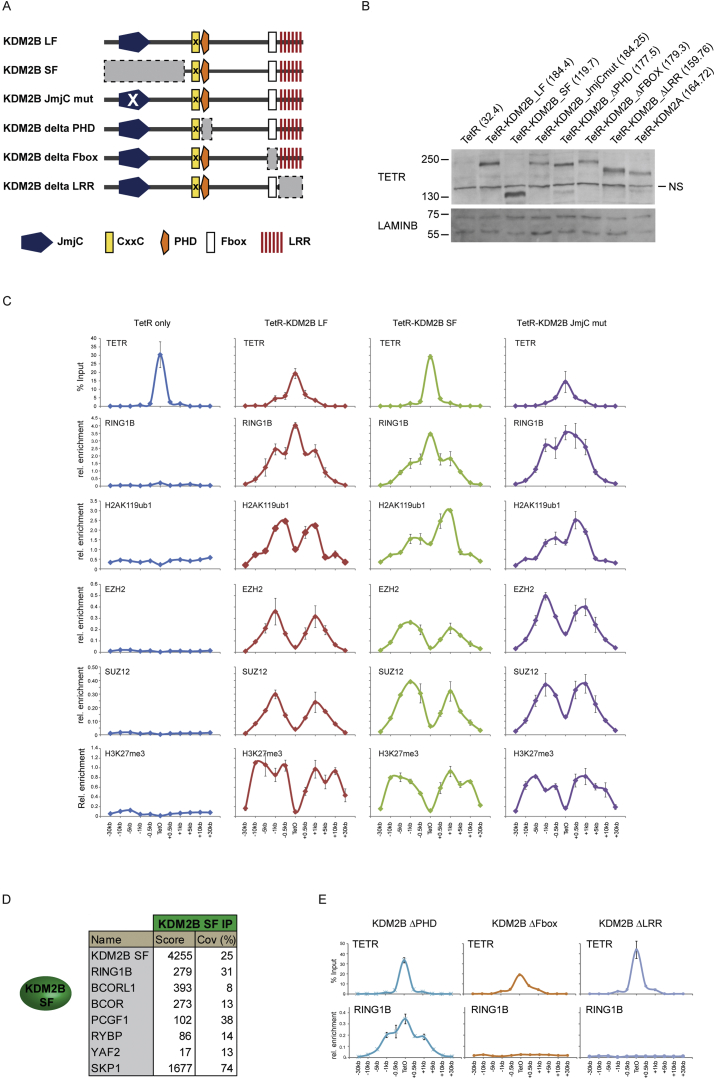
(A) KDM2B long form (LF) and short form (SF) with their domain organization indicated. Additional, TetR fusion constructs which have had domains removed (gray boxes) or mutated are indicated.
(B) Western blot analysis of the TetR-KDM2B fusion cell lines indicating roughly equal protein expression.
(C) ChIP-qPCR analysis for the TetR fusion protein, RING1B, H2AK119ub1, SUZ12, EZH2, and H3K27me3 across the TetO containing region in the TetR only, TetR-KDM2B LF, TetR-KDM2B SF, and TetR-KDM2B LF demethylase mutant (JmjC mutant). All three versions of KDM2B lead to efficient RING1B recruitment, H2AK119ub1, and formation of a polycomb domain containing SUZ12, EZH2, and H3K27me3. This indicates that both forms of KDM2B can form polycomb domains independent of their demethylase activity.
(D) An epitope tagged version of the KDM2B-SF was stably expressed in mouse ESCs, affinity purified, and associated proteins identified by tandem mass spectrometry. This revealed that the short form of KDM2B forms the same variant PRC1 complex as the long form of the protein, consistent with its capacity to recruit RING1B and form polycomb domains in tethering assays.
(E) Based on the capacity of KDM2B-SF to associate with the PCGF1/PRC1 complex (D) the domain(s) mediating this were further mapped in tethering assays. The C-terminal Fbox and LRR domains are required for RING1B recruitment whereas the PHD domain is dispensable.