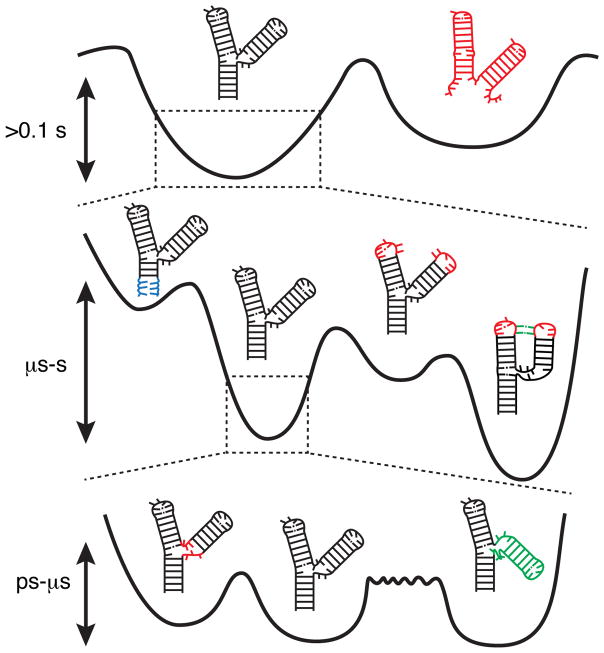
Figure 1.
The different tiers of RNA dynamics. At the lowest level of the hierarchy are secondary structure dynamics, which define broad free energy basins with high separating barriers. Within each secondary structure are smaller alternative base pairing arrangements that define Tier 1 dynamics. These include base pair melting (blue, left), reshuffling (middle right, red), and tertiary pairing (green). Each local pairing basin in turn defines a limited set of 3D conformations, transitions between which comprise Tier 2 dynamics. These dynamics include loop dynamics (left, red) and inter-helical dynamics (right, green). Although inter-helical and loop-dynamics have similar barrier heights, due to the larger number of involved coordinates inter-helical dynamics typically proceed more slowly (long rough separating barrier).