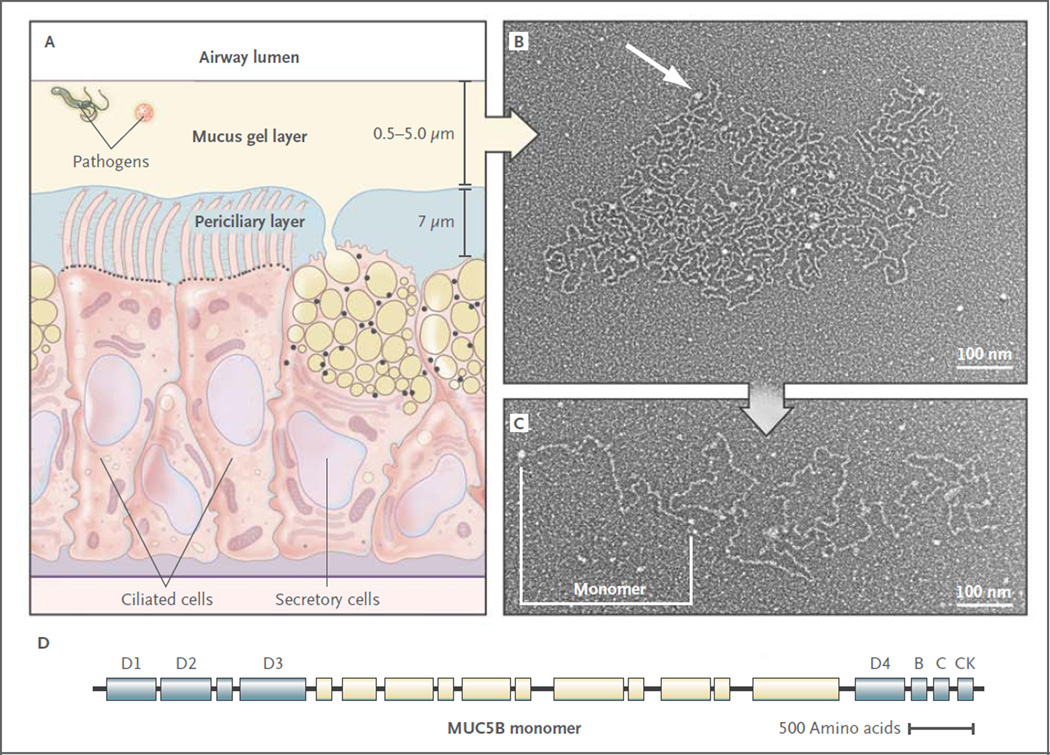
Figure 2. Structure of Airway Mucus.
Panel A shows a distal bronchus with a single layer of columnar epithelial cells. The ciliated cells express approximately 200 cilia that are about 7 µm in length. The secretory cells show mixed features of Clara cells (small, black, apical granules containing proteins) and goblet cells (large granules up to 1 µm in diameter containing yellow mucins and black proteins). The mucus gel layer increases in thickness from distal to proximal airways, whereas the periciliary layer is approximately 7 µm deep throughout the conducting airways. Panel B shows an electron micrograph of a partially expanded MUC5B polymer after secretion, intermediate between its condensed form within a secretory granule and its expanded linear structure.9 Nodes where monomers are bonded appear as white globules (arrow). Panel C shows an electron micrograph of an extended MUC5B polymer. A MUC5B monomer is approximately 450 nm in length, and polymers contain 2 to 20 subunits. Panel D shows the structure of MUC5B. It is organized into an N-terminal region containing von Willebrand factor D1–3 domains involved in N–N polymerization (blue), a central region containing glycosylated mucin domains (pale yellow), and a C-terminal region containing von Willebrand factor D4, B, C, and CK domains involved in C-C polymerization.1,3 The structure of MUC5A is similar (not shown). Electron micrographs provided courtesy of Mehmet Kesimer and John K. Sheehan, University of North Carolina.