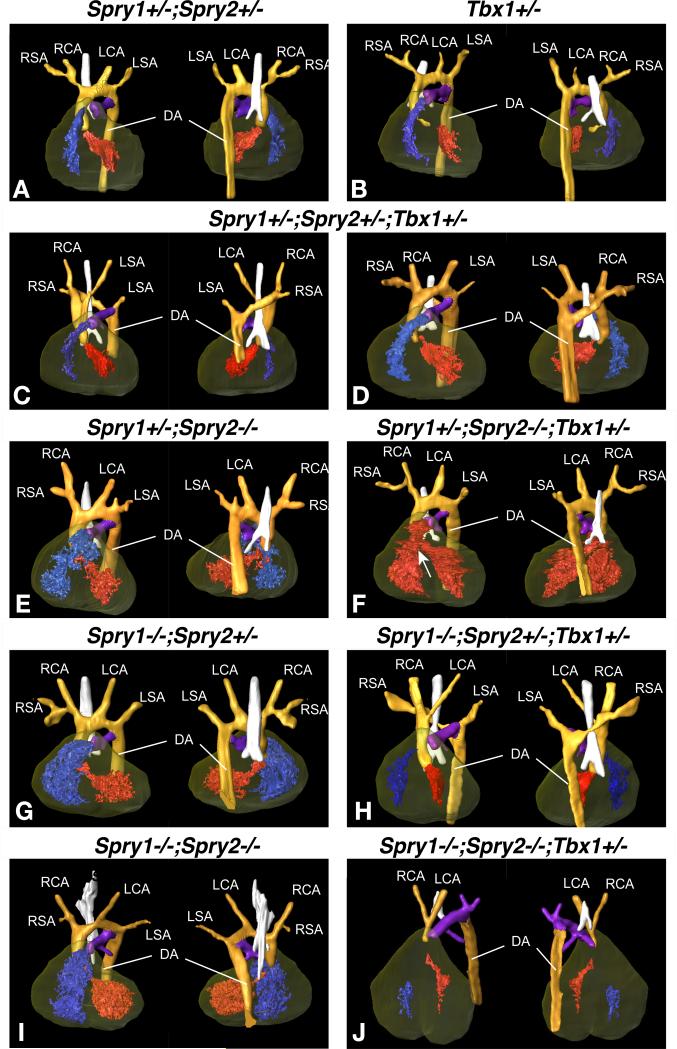
Figure 4. Anatomy of the great arteries as determined by micro MRI scans of E14.5 embryos.
3D reconstruction of high resolution MRI data from E15.5 embryos (Amira® software, Visage Imaging Inc.) showing the great arteries. Ventral (left) and dorsal (right) views are shown for each genotype indicated. Individual structures are coloured as follows: orange for the aortic arch and descending aorta, purple for the pulmonary artery, the trachea is highlighted in white and the heart is shaded in brown with the right ventricle in blue and the left ventricle in red. Where there is a ventricular septal defect (VSD), both ventricles are in red. Arteries are labelled as LSA: Left Subclavian Artery, LCA: Left Common Carotid Artery, RSA: Right Subclavian Artery, RCA: Right Common Carotid Artery and DA: Descending Aorta.
A) Spry1+/-;Spry2+/- control embryo and (B) Tbx1+/- embryo with normal arteries and normal heart.
C, D) Examples of Spry1+/-;Spry2+/-;Tbx1+/- embryos with normal vessels (C) or retroesophageal aortic arch (REAA) and aortic vascular ring (D).
E,G,I) Compound Spry1;Spry2 mutant embryos with normal anatomy.
F) Spry1+/-;Spry2-/-;Tbx1+/- embryo with normal arteries and a ventricular septal defect (VSD, indicated by an arrow). Both ventricles are coloured in red to indicate mixing of oxygenated and de-oxygenated blood due to the VSD.
H) Spry1-/-;Spry2+/-;Tbx1+/- embryo with REAA.
J) Spry1-/-;Spry2-/-;Tbx1+/- embryo with interrupted aortic arch type B (IAA-B).