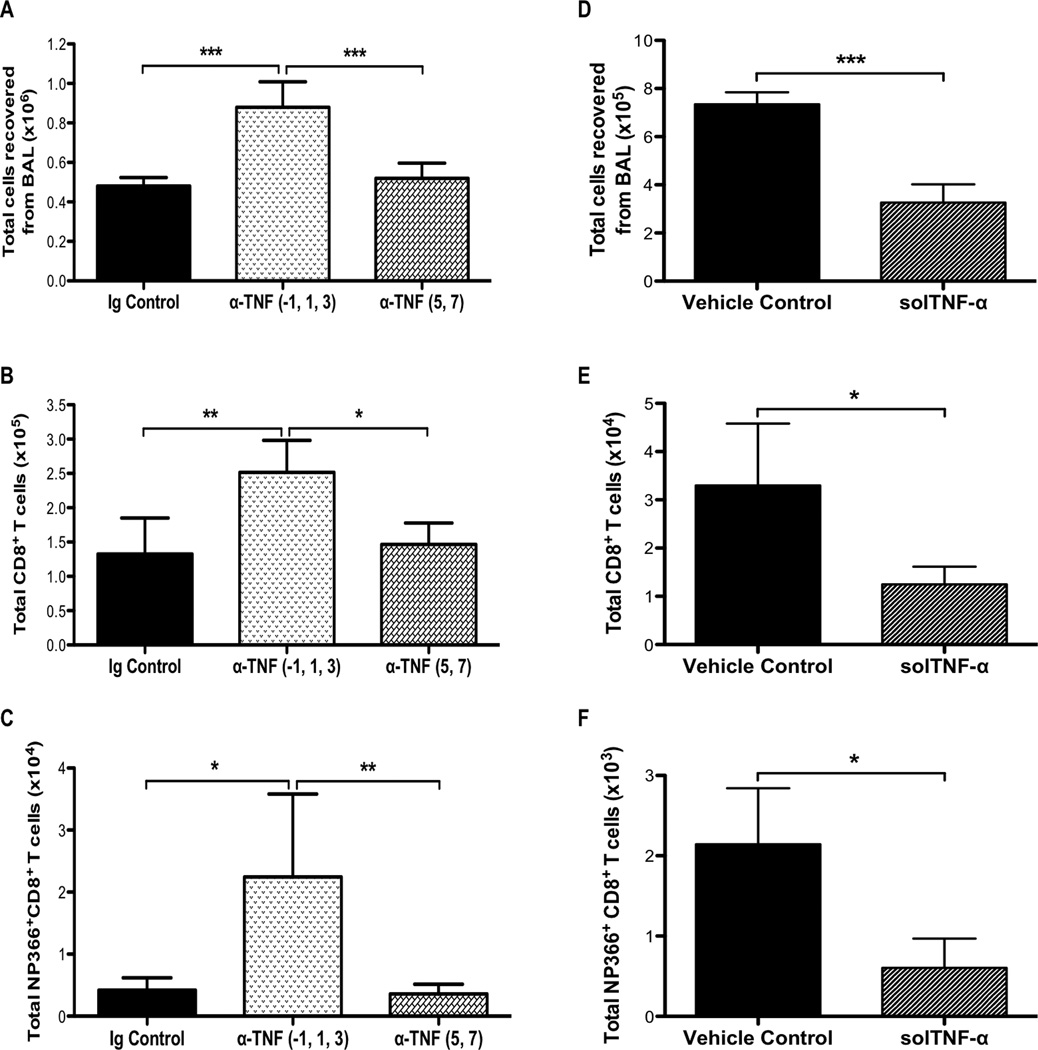
Figure 8. TNF-α expression is required early during infection to limit the size of the T-cell response.
WT mice received anti-TNF-α or IgG1 control by intraperitoneal injection on days −1, 1, and 3 or days 5 and 7 post-infection. (A) Total number of viable cells recovered from the airways 8 days post-infection. Flow cytometry was used to analyze the total number of (B) CD8+ and (C) NP366–374-specific CD8+ T cells. (D) Alternatively, memTNFΔ1–9, K11E KI mice were intranasally administered 2µg mouse recombinant solTNF-α at the time of infection and the total number of viable cells from the airways was enumerated on day 8 post-infection. Flow cytometry was used to analyze the total number of (E) CD8+ and (F) NP366–374-specific CD8+ T cells. Data represents mean ± standard deviation. Each group consists of 3–5 mice per group. Data are representative of two independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005.